Calcium inhibits bap-dependent multicellular behavior in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 15516560
- PMCID: PMC524893
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.22.7490-7498.2004
Calcium inhibits bap-dependent multicellular behavior in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
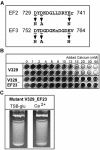
Bap (biofilm-associated protein) is a 254-kDa staphylococcal surface protein implicated in formation of biofilms by staphylococci isolated from chronic mastitis infections. The presence of potential EF-hand motifs in the amino acid sequence of Bap prompted us to investigate the effect of calcium on the multicellular behavior of Bap-expressing staphylococci. We found that addition of millimolar amounts of calcium to the growth media inhibited intercellular adhesion of and biofilm formation by Bap-positive strain V329. Addition of manganese, but not addition of magnesium, also inhibited biofilm formation, whereas bacterial aggregation in liquid media was greatly enhanced by metal-chelating agents. In contrast, calcium or chelating agents had virtually no effect on the aggregation of Bap-deficient strain M556. The biofilm elicited by insertion of bap into the chromosome of a biofilm-negative strain exhibited a similar dependence on the calcium concentration, indicating that the observed calcium inhibition was an inherent property of the Bap-mediated biofilms. Site-directed mutagenesis of two of the putative EF-hand domains resulted in a mutant strain that was capable of forming a biofilm but whose biofilm was not inhibited by calcium. Our results indicate that Bap binds Ca2+ with low affinity and that Ca2+ binding renders the protein noncompetent for biofilm formation and for intercellular adhesion. The fact that calcium inhibition of Bap-mediated multicellular behavior takes place in vitro at concentrations similar to those found in milk serum supports the possibility that this inhibition is relevant to the pathogenesis and/or epidemiology of the bacteria in the mastitis process.
Figures






References
-
- Alais, C. 1984. Science du lait: principes des techniques laitières, 4th ed. SEPAIC, Paris, France.
-
- Blood, D. C., J. H. Arundel, C. C. Gay, J. A. Henderson, and O. M. Radostits. 1979. Veterinary medicine: a textbook of the diseases of cattle, sheep, pigs and horses. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
-
- Bootman, M. D., and M. J. Berridge. 1995. The elemental principles of calcium signaling. Cell 83:675-678. - PubMed
-
- Brown, E. M., P. M. Vassilev, and S. C. Hebert. 1995. Calcium ions as extracellular messengers. Cell 83:679-682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

