Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 15518235
- PMCID: PMC2504526
- DOI: 10.1080/08977190410001723308
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
Since the purification of BDNF in 1982, a great deal of evidence has mounted for its central roles in brain development, physiology, and pathology. Aside from its importance in neural development and cell survival, BDNF appears essential to molecular mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. Basic activity-related changes in the central nervous system are thought to depend on BDNF modification of synaptic transmission, especially in the hippocampus and neocortex. Pathologic levels of BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity may contribute to conditions such as epilepsy and chronic pain sensitization, whereas application of the trophic properties of BDNF may lead to novel therapeutic options in neurodegenerative diseases and perhaps even in neuropsychiatric disorders.
Figures
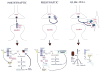
References
-
- Acheson A, et al. A BDNF autocrine loop in adult sensory neurons prevents cell death. Nature. 1995;374:450–453. - PubMed
-
- Alderson RF, et al. Truncated TrkB mediates the endocytosis and release of BDNF and neurotrophin-4/5 by rat astrocytes and schwann cells in vitro. Brain Res. 2000;871:210–222. - PubMed
-
- Alonso M, et al. BDNF-triggered events in the rat hippocampus are required for both short- and long-term memory formation. Hippocampus. 2002;12:551–560. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA. Neurotrophins and depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999;20:59–61. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA, DiStefano PS. Neurotrophin trafficking by anterograde transport. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:431–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
