Kinin B1 receptors: key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes
- PMID: 15520046
- PMCID: PMC1575942
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706012
Kinin B1 receptors: key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes
Abstract
Kinins are a family of peptides implicated in several pathophysiological events. Most of their effects are likely mediated by the activation of two G-protein-coupled receptors: B(1) and B(2). Whereas B(2) receptors are constitutive entities, B(1) receptors behave as key inducible molecules that may be upregulated under some special circumstances. In this context, several recent reports have investigated the importance of B(1) receptor activation in certain disease models. Furthermore, research on B(1) receptors in the last years has been mainly focused in determining the mechanisms and pathways involved in the process of induction. This was essentially favoured by the advances obtained in molecular biology studies, as well as in the design of selective and stable peptide and nonpeptide kinin B(1) receptor antagonists. Likewise, development of kinin B(1) receptor knockout mice greatly helped to extend the evidence about the relevance of B(1) receptors during pathological states. In the present review, we attempted to remark the main advances achieved in the last 5 years about the participation of kinin B(1) receptors in painful and inflammatory disorders. We have also aimed to point out some groups of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, arthritis, cancer or neuropathic pain, in which the strategic development of nonpeptidic oral-available and selective B(1) receptor antagonists could have a potential relevant therapeutic interest.
Figures
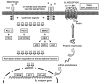
References
-
- AHLUWALIA A., PERRETTI M. B1 receptors as a new inflammatory target. Could this B the 1. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999;20:100–104. - PubMed
-
- AKIRA S., YAMAMOTO M., TAKEDA K. Role of adapters in Toll-like receptor signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003;31:637–642. - PubMed
-
- ANGERS M., DROUIN R., BACHVAROVA M., PARADIS I., MARCEAU F., BACHVAROV D.R. In vivo protein-DNA interactions at the kinin B1 receptor gene promoter: no modification on interleukin-1 beta or lypopolysaccharide induction. J. Cell. Biochem. 2000;78:278–296. - PubMed
-
- BACHAR O., ADNER M., UDDMAN R., CARDELL L.O. Toll-like receptor stimulation induces airway hyper-responsiveness to bradykinin, an effect mediated by JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004;34:1196–1207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

