A cell sizer network involving Cln3 and Far1 controls entrance into S phase in the mitotic cycle of budding yeast
- PMID: 15520229
- PMCID: PMC2172493
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200405102
A cell sizer network involving Cln3 and Far1 controls entrance into S phase in the mitotic cycle of budding yeast
Abstract
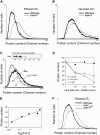
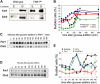
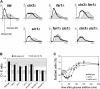
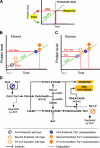
Saccharomyces cerevisiae must reach a carbon source-modulated critical cell size, protein content per cell at the onset of DNA replication (Ps), in order to enter S phase. Cells grown in glucose are larger than cells grown in ethanol. Here, we show that an increased level of the cyclin-dependent inhibitor Far1 increases cell size, whereas far1 Delta cells start bud emergence and DNA replication at a smaller size than wild type. Cln3 Delta, far1 Delta, and strains overexpressing Far1 do not delay budding during an ethanol glucose shift-up as wild type does. Together, these findings indicate that Cln3 has to overcome Far1 to trigger Cln-Cdc28 activation, which then turns on SBF- and MBF-dependent transcription. We show that a second threshold is required together with the Cln3/Far1 threshold for carbon source modulation of Ps. A new molecular network accounting for the setting of Ps is proposed.
Figures


References
-
- Alberghina, L., and D. Porro. 1993. Quantitative flow cytometry: analysis of protein distributions in budding yeast. A mini-review. Yeast. 9:815–823. - PubMed
-
- Alberghina, L., D. Porro, and L. Cazzador. 2001. Towards a blueprint of the cell cycle. Oncogene. 20:1128–1134. - PubMed
-
- Baroni, M.D., P. Monti, G. Marconi, and L. Alberghina. 1992. cAMP-mediated increase in the critical cell size required for the G1 to S transition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp. Cell Res. 201:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

