Idling by DNA polymerase delta maintains a ligatable nick during lagging-strand DNA replication
- PMID: 15520275
- PMCID: PMC528896
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1252304
Idling by DNA polymerase delta maintains a ligatable nick during lagging-strand DNA replication
Abstract
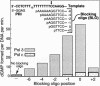
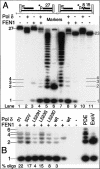
During each yeast cell cycle, approximately 100,000 nicks are generated during lagging-strand DNA replication. Efficient nick processing during Okazaki fragment maturation requires the coordinated action of DNA polymerase delta (Pol delta) and the FLAP endonuclease FEN1. Misregulation of this process leads to the accumulation of double-stranded breaks and cell lethality. Our studies highlight a remarkably efficient mechanism for Okazaki fragment maturation in which Pol delta by default displaces 2-3 nt of any downstream RNA or DNA it encounters. In the presence of FEN1, efficient nick translation ensues, whereby a mixture of mono- and small oligonucleotides are released. If FEN1 is absent or not optimally functional, the ability of Pol delta to back up via its 3'-5'-exonuclease activity, a process called idling, maintains the polymerase at a position that is ideal either for ligation (in case of a DNA-DNA nick) or for subsequent engagement by FEN1 (in case of a DNA-RNA nick). Consistent with the hypothesis that DNA polymerase epsilon is the leading-strand enzyme, we observed no idling by this enzyme and no cooperation with FEN1 for creating a ligatable nick.
Figures



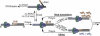
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of enzymatic interactions during short flap human Okazaki fragment processing by two forms of human DNA polymerase δ.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Nov;12(11):922-35. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Sep 10. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 24035200 Free PMC article.
-
The 3'-->5' exonuclease of DNA polymerase delta can substitute for the 5' flap endonuclease Rad27/Fen1 in processing Okazaki fragments and preventing genome instability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):5122-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091095198. Epub 2001 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11309502 Free PMC article.
-
Okazaki fragment maturation in yeast. II. Cooperation between the polymerase and 3'-5'-exonuclease activities of Pol delta in the creation of a ligatable nick.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 17;278(3):1626-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209803200. Epub 2002 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12424237
-
Polymerase dynamics at the eukaryotic DNA replication fork.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 13;284(7):4041-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800062200. Epub 2008 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 18835809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Okazaki fragment maturation: nucleases take centre stage.J Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;3(1):23-30. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjq048. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21278448 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase γ is required for ligation during mitochondrial DNA replication.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 22;6:7303. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8303. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26095671 Free PMC article.
-
Bypass of DNA interstrand crosslinks by a Rev1-DNA polymerase ζ complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 4;48(15):8461-8473. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa580. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32633759 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage tolerance pathway involving DNA polymerase ι and the tumor suppressor p53 regulates DNA replication fork progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 26;113(30):E4311-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605828113. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27407148 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid: a new phenotype to probe DNA polymerase delta in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2005 Jun;170(2):569-80. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.040295. Epub 2005 Mar 31. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15802517 Free PMC article.
-
Damage-specific modification of PCNA.Cell Cycle. 2010 Sep 15;9(18):3674-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.18.13121. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20930510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayyagari R., Gomes, X.V., Gordenin, D.A., and Burgers, P.M. 2003. Okazaki fragment maturation in yeast. I. Distribution of functions between FEN1 and DNA2. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 1618-1625. - PubMed
-
- Bae S.H., Bae, K.H., Kim, J.A., and Seo, Y.S. 2001. RPA governs endonuclease switching during processing of Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes. Nature 412: 456-461. - PubMed
-
- Bae S.H., Kim, D.W., Kim, J., Kim, J.H., Kim, D.H., Kim, H.D., Kang, H.Y., and Seo, Y.S. 2002. Coupling of DNA helicase and endonuclease activities of yeast Dna2 facilitates Okazaki fragment processing. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 26632-26641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
