CTD kinase I is involved in RNA polymerase I transcription
- PMID: 15520468
- PMCID: PMC528809
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh927
CTD kinase I is involved in RNA polymerase I transcription
Abstract
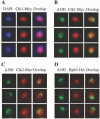
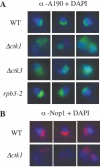
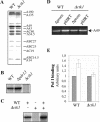
RNA polymerase II carboxy terminal domain (CTD) kinases are key elements in the control of mRNA synthesis. Yeast CTD kinase I (CTDK-I), is a non-essential complex involved in the regulation of mRNA synthesis at the level of transcription elongation, pre-mRNA 3' formation and nuclear export. Here, we report that CTDK-I is also involved in ribosomal RNA synthesis. We show that CTDK-I is localized in part in the nucleolus. In its absence, nucleolar structure and RNA polymerase I transcription are affected. In vitro experiments show an impairment of the Pol I transcription machinery. Remarkably, RNA polymerase I co-precipitates from cellular extracts with Ctk1, the kinase subunit of the CTDK-I complex. In vitro analysis further demonstrates a direct interaction between RNA polymerase I and Ctk1. The results suggest that CTDK-I might participate in the regulation of distinct nuclear transcriptional machineries, thus playing a role in the adaptation of the global transcriptional response to growth signalling.
Figures

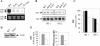
Similar articles
-
CTD kinase I is required for the integrity of the rDNA tandem array.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4996-5006. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl493. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16984969 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of CTDK-I throughout the cell.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jul;76(14):2789-2797. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03118-0. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31037337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and activation mechanism of the yeast RNA Pol II CTD kinase CTDK-1 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 19;118(3):e2019163118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2019163118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33431688 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of yeast carboxy-terminal domain kinase I (CTDK-I) in transcription elongation in vivo.Gene. 2001 Apr 4;267(1):31-6. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00389-4. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11311553
-
Emerging roles for RNA polymerase II CTD in Arabidopsis.Trends Plant Sci. 2013 Nov;18(11):633-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Trends Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23910452 Review.
Cited by
-
Ctk1 function is necessary for full translation initiation activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Jan;14(1):86-95. doi: 10.1128/EC.00106-14. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25416238 Free PMC article.
-
P-TEFb Kinase Activity Is Essential for Global Transcription, Resumption of Meiosis and Embryonic Genome Activation in Pig.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152254. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27011207 Free PMC article.
-
The Paf1 complex is required for efficient transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 17;106(7):2153-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812939106. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19164765 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinases: Masters of the eukaryotic universe.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Sep 17;15(1):e1816. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1816. Online ahead of print. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 37718413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I is linked to efficient rRNA processing and ribosome assembly.Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 27;26(2):217-29. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.04.007. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17466624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sentenac A. (1985) Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem., 18, 31–90. - PubMed
-
- Warner J.R. (1999) The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast. Trends Biochem. Sci., 24, 437–440. - PubMed
-
- Nomura M. (1998) Transcription factors used by Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase I and the mechanism of initiation. In Paule,M.R. (ed.), Transcription of Ribosomal RNA Genes by Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase I. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp. 155–172.
-
- Keys D.A., Lee,B.S., Dodd,J.A., Nguyen,T.T., Vu,L., Fantino,E., Burson,L.M., Nogi,Y. and Nomura,M. (1996) Multiprotein transcription factor UAF interacts with the upstream element of the yeast RNA polymerase I promoter and forms a stable preinitiation complex. Genes Dev., 10, 887–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

