Qa-1 restriction of CD8+ suppressor T cells
- PMID: 15520850
- PMCID: PMC524234
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23152
Qa-1 restriction of CD8+ suppressor T cells
Abstract
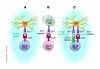
There is increasing evidence that the immune response can be inhibited by several T cell subsets, including NK T cells, CD25+CD4+ T cells, and a subpopulation of CD8+ T cells. Animal model studies of multiple sclerosis have suggested an important role for suppressor CD8+ T cells in protection against disease recurrence and exacerbation. The molecular lynchpin of CD8+ suppressive activity is the murine MHC molecule Qa-1, termed HLA-E in humans. Here we summarize findings from work on Qa-1 that have begun to delineate suppressor CD8+ T cells and their mechanisms of action in the context of self tolerance and autoimmune disease.
Figures
References
-
- Cantor H. T-cell receptor crossreactivity and autoimmune disease. Adv. Immunol. 2000;75:209–233. - PubMed
-
- Goldrath AW, Bevan MJ. Selecting and maintaining a diverse T-cell repertoire. Nature. 1999;402:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Bouneaud C, Kourilsky P, Bousso P. Impact of negative selection on the T cell repertoire reactive to a self-peptide: a large fraction of T cell clones escapes clonal deletion. Immunity. 2000;13:829–840. - PubMed
-
- Slifka MK, et al. Preferential escape of subdominant CD8+ T cells during negative selection results in an altered antiviral T cell hierarchy. J. Immunol. 2003;170:1231–1239. - PubMed
-
- Kearney ER, Pape KA, Loh DY, Jenkins MK. Visualization of peptide-specific T cell immunity and peripheral tolerance induction in vivo. Immunity. 1994;1:327–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

