p16 and ARF: activation of teenage proteins in old age
- PMID: 15520854
- PMCID: PMC524239
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23437
p16 and ARF: activation of teenage proteins in old age
Abstract
Cellular senescence induced by different stresses and telomere shortening appears to play an important role in the aging process. The products of the INK4a/ARF locus--p16INK4a and ARF--arrest cell proliferation at the senescence stage by exerting their effects on retinoblastoma protein- and p53-mediated responsive pathways. A study in this issue of the JCI provides experimental evidence of a specific upregulation of these cell cycle inhibitors in a variety of organs during mammalian aging.
Figures
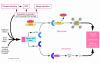
Comment on
-
Ink4a/Arf expression is a biomarker of aging.J Clin Invest. 2004 Nov;114(9):1299-307. doi: 10.1172/JCI22475. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15520862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim S, Kaminker P, Campisi J. Telomeres, aging and cancer: in search of a happy ending. Oncogene. 2002;21:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Sharpless NE, DePinho RA. p53: good cop/bad cop. Cell. 2002;110:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Campisi J. The biology of replicative senescence. Eur. J. Cancer. 1997;33:703–709. - PubMed
-
- Reaper PM, di Fagagna F, Jackson SP. Activation of the DNA damage response by telomere attrition: a passage to cellular senescence. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:543–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

