Mitochondrial remodeling in adipose tissue associated with obesity and treatment with rosiglitazone
- PMID: 15520860
- PMCID: PMC524228
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI21752
Mitochondrial remodeling in adipose tissue associated with obesity and treatment with rosiglitazone
Abstract
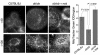
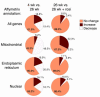
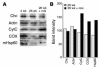
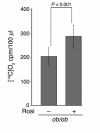
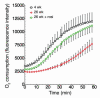
Adipose tissue plays a central role in the control of energy homeostasis through the storage and turnover of triglycerides and through the secretion of factors that affect satiety and fuel utilization. Agents that enhance insulin sensitivity, such as rosiglitazone, appear to exert their therapeutic effect through adipose tissue, but the precise mechanisms of their actions are unclear. Rosiglitazone changes the morphological features and protein profiles of mitochondria in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. To examine the relevance of these effects in vivo, we studied white adipocytes from ob/ob mice during the development of obesity and after treatment with rosiglitazone. The levels of approximately 50% of gene transcripts encoding mitochondrial proteins were decreased with the onset of obesity. About half of those genes were upregulated after treatment with rosiglitazone, and this was accompanied by an increase in mitochondrial mass and changes in mitochondrial structure. Functionally, adipocytes from rosiglitazone-treated mice displayed markedly enhanced oxygen consumption and significantly increased palmitate oxidation. These data reveal mitochondrial remodeling and increased energy expenditure in white fat in response to rosiglitazone treatment in vivo and suggest that enhanced lipid utilization in this tissue may affect whole-body energy homeostasis and insulin sensitivity.
Figures



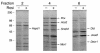

References
-
- Argyropoulos G, Harper ME. Uncoupling proteins and thermoregulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002;92:2187–2198. - PubMed
-
- Cannon B, Nedergaard J. Brown adipose tissue: function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004;84:277–359. - PubMed
-
- Rajala MW, Scherer PE. Minireview: the adipocyte—at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3765–3773. - PubMed
-
- Friedman JM. The function of leptin in nutrition, weight, and physiology. Nutr. Rev. 2002;60:S1–S14; discussion S68–S84, S85–S17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

