Imatinib mesylate inhibits the profibrogenic activity of TGF-beta and prevents bleomycin-mediated lung fibrosis
- PMID: 15520863
- PMCID: PMC524221
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19603
Imatinib mesylate inhibits the profibrogenic activity of TGF-beta and prevents bleomycin-mediated lung fibrosis
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a progressive and fatal fibrotic disease of the lungs with unclear etiology. Prior efforts to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis that focused on anti-inflammatory therapy have not proven to be effective. Recent insight suggests that the pathogenesis is mediated through foci of dysregulated fibroblasts driven by profibrotic cytokine signaling. TGF-beta and PDGF are 2 of the most potent of these cytokines. In the current study, we investigated the role of TGF-beta-induced fibrosis mediated by activation of the Abelson (Abl) tyrosine kinase. Our data indicate that fibroblasts respond to TGF-beta by stimulating c-Abl kinase activity independently of Smad2/3 phosphorylation or PDGFR activation. Moreover, inhibition of c-Abl by imatinib prevented TGF-beta-induced ECM gene expression, morphologic transformation, and cell proliferation independently of any effect on Smad signaling. Further, using a mouse model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, we found a significant inhibition of lung fibrosis by imatinib. Thus, Abl family members represent common targets for the modulation of profibrotic cytokine signaling.
Figures

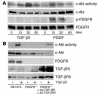

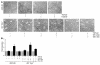
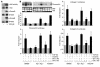
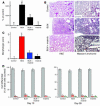
References
-
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000;161:646–664. - PubMed
-
- Coultas DB, Sumwalt RE, Black WC, Sobonya RE. The epidemiology of interstitial lung diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994;150:967–972. - PubMed
-
- Bjoraker JA, et al. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998;157:199–203. - PubMed
-
- Strieter RM. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis: conference summary. Chest. 2001;120(1 Suppl.):77S–85S. - PubMed
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

