Mapping of a major locus that determines telomere length in humans
- PMID: 15520935
- PMCID: PMC1196417
- DOI: 10.1086/426734
Mapping of a major locus that determines telomere length in humans
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Feb;76(2):373
Abstract
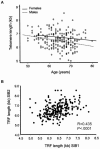
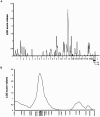
Telomere length is a crucial factor for both normal chromosomal function and senescence. Mean telomere length in humans shows considerable interindividual variation and strong genetic determination. To see if a locus (or loci) affecting telomere length in humans could be mapped, we performed a quantitative-trait linkage analysis of mean leukocyte telomere-restriction-fragment (TRF) lengths, measured by Southern blotting, in 383 adult subjects comprising 258 sib pairs. Heritability of mean (+/-SE) TRF was 81.9%+/-11.8%. There was significant linkage (LOD score 3.20) of mean TRF length to a locus on chromosome 12, which explained 49% of the overall variability in mean TRF length. We present preliminary analysis of a strong candidate gene in the region, the DNA helicase DDX11. In conclusion, we report mapping of the first locus that determines mean telomere length in humans. Identification of the gene involved and elucidation of its mechanism of action could have important implications for our understanding of chromosomal assembly, telomere biology, and susceptibility to age-related diseases.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Ensembl, http://www.ensembl.org/ (for genetic distance between markers and identification of genes in the interval of interest)
-
- HapMap Project, http://www.hapmap.org/ (for SNP information)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for DDX11) - PubMed
-
- SNP Consortium Database, http://snp.cshl.org (for SNP information)
References
-
- Benetos A, Okuda K, Lajemi M, Kimura M, Thomas F, Skurnick J, Labat C, Bean K, Aviv A (2001) Telomere length as an indicator of biological aging: the gender effect and relation with pulse pressure and pulse wave velocity. Hypertension 37:381–385 - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Goring HH, Ott J (1997) Relationship estimation in affected sib pair analysis of late-onset diseases. Eur J Hum Genet 5:69–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

