DNA delivery from hyaluronic acid-collagen hydrogels via a substrate-mediated approach
- PMID: 15522759
- PMCID: PMC2648403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.05.007
DNA delivery from hyaluronic acid-collagen hydrogels via a substrate-mediated approach
Abstract
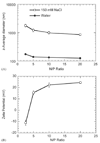
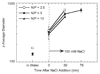
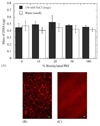
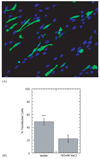
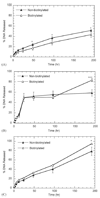
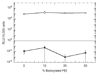
Efficient and controlled gene delivery from biodegradable materials can be employed to stimulate cellular processes that lead to tissue regeneration. In this report, a substrate-mediated approach was developed to deliver DNA from hyaluronic acid-collagen hydrogels. The hydrogels were formed by crosslinking HA with poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether. Poly(ethylene imine)(PEI)/DNA complexes were immobilized to the substrate using either biotin/neutravidin or non-specific adsorption. Complexes were formed in the presence or absence of salt to regulate complex size, and resulted in complexes with z-average diameters of 1221.7 +/- 152.3 and 139.4 +/- 1.3 nm, respectively. During 48-h incubation in PBS or hyaluronidase, DNA was released slowly from the hydrogel substrate (<30% of immobilized DNA), which was enhanced by incubation with conditioned media (approximately 50% of immobilized DNA). Transgene expression mediated by immobilized, large diameter complexes was 3 to 7-fold greater than for small diameter complexes. However, the percentage of cells expressing the transgene was greater for small diameter complexes (48.7%) than for large diameter complexes (22.3%). Spatially controlled gene transfer was achieved by topographically patterning the hydrogel to pattern cell adhesion. Biomaterial-based gene delivery can be applicable to numerous tissue engineering applications, or as a tool to examine tissue formation.
Figures



References
-
- Kabanov AV, Kabanov VA. DNA complexes with polycations for the delivery of genetic material into cells. Bioconjug Chem. 1995;6(1):7–20. - PubMed
-
- Shea LD, Smiley E, Bonadio J, Mooney DJ. DNA delivery from polymer matrices for tissue engineering. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17(6):551–554. - PubMed
-
- Williams DA. Retroviral-bronectin interactions in transduction of mammalian cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;872:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Levy RJ, Song C, Tallapragada S, DeFelice S, Hinson JT, Vyavahare N, et al. Localized adenovirus gene delivery using antiviral IgG complexation. Gene Ther. 2001;8(9):659–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

