Palliation of soft tissue cancer pain with radiofrequency ablation
- PMID: 15524075
- PMCID: PMC2408960
Palliation of soft tissue cancer pain with radiofrequency ablation
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to analyze the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) to treat pain from soft tissue neoplasms. RFA was performed on 15 painful soft tissue tumors in 14 patients. Tumors varied in histology and location and ranged in size from 2 to 20 cm. Patient pain was assessed using the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) at baseline and 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, and 3 months post RFA. All patients had unresectable tumors or were poor operative candidates whose pain was poorly controlled by conventional treatment methods. BPI scores were divided into two categories: pain severity and interference of pain. Although not all scores were statistically significant, all mean scores trended down with increased time post ablation. Based on these outcomes, RFA appears to be a low-risk and well-tolerated procedure for pain palliation in patients with unresectable, painful soft tissue neoplasms. RFA is effective for short-term local pain control and may provide another option for failed chemotherapy or radiation therapy in patients with cancer. However, pain may transiently worsen, and relief is often temporary.
Figures
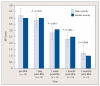

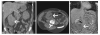

Similar articles
-
Radiofrequency Ablation Provides Rapid and Durable Pain Relief for the Palliative Treatment of Lytic Bone Metastases Independent of Radiation Therapy: Final Results from the OsteoCool Tumor Ablation Post-Market Study.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2023 May;46(5):600-609. doi: 10.1007/s00270-023-03417-x. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37012392 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral and soft-tissue tumors: radiofrequency and alcohol ablation for pain relief--initial experience.Radiology. 2008 Sep;248(3):1067-76. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2483061883. Radiology. 2008. PMID: 18710995 Clinical Trial.
-
Radiofrequency ablation of bone metastases induces long-lasting palliation in patients with untreatable cancer.Singapore Med J. 2008 Jul;49(7):565-70. Singapore Med J. 2008. PMID: 18695866
-
The role and limitations of radiofrequency ablation in treatment of bone and soft tissue tumors.Curr Oncol Rep. 2004 Jul;6(4):315-20. doi: 10.1007/s11912-004-0042-1. Curr Oncol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15161588 Review.
-
Radiofrequency ablation of osseous metastases for the palliation of pain.Skeletal Radiol. 2008 Mar;37(3):189-94. doi: 10.1007/s00256-007-0404-5. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Skeletal Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18030464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Palliative radiofrequency ablation for recurrent prostate cancer.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006 May-Jun;29(3):482-5. doi: 10.1007/s00270-004-0200-8. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006. PMID: 16010507 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Microwave Ablation and Osteosynthesis for Long Bone Metastases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Aug 16;57(8):825. doi: 10.3390/medicina57080825. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34441031 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed radiofrequency treatment of pain relieving point in a soft tissue.Korean J Pain. 2011 Mar;24(1):57-60. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.57. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Korean J Pain. 2011. PMID: 21390181 Free PMC article.
-
Subdermal fluid for skin protection during superficial palliative thermal ablation.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006 Sep;17(9):1545-7. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000232496.73682.00. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006. PMID: 16990478 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Radiofrequency ablation: a nursing perspective.Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2005 Jun;9(3):346-9. doi: 10.1188/05.CJON.346-349. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2005. PMID: 15973845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levy MH, Rosen SM, Ottery FD, Hermann J. Supportive care in oncology. Curr Probl Cancer. 1992;16:329–418. - PubMed
-
- Onofrio BM. Radiofrequency percutaneous gasserian ganglion lesions: results in 140 patients with trigeminal pain. J Neurosurg. 1975;42:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Slappendel R, Crul BJ, Braak GJ, et al. The efficacy of radiofrequency lesioning of the cervical spinal dorsal root ganglion in a double blinded randomized study: no difference between 40 degrees C and 67 degrees C treatments. Pain. 1997;73:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Sanders M, Zuurmond WW. Efficacy of spheno-palatine ganglion blockade in 66 patients suffering from cluster headache: a 12- to 70-month follow-up evaluation. J Neurosurg. 1997;87:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Sollitto RJ, Plotkin E, Klein PG, Mullin P. Early clinical results of the use of radiofrequency lesioning in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1997;36:215–219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
