Axin stimulates p53 functions by activation of HIPK2 kinase through multimeric complex formation
- PMID: 15526030
- PMCID: PMC533058
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600475
Axin stimulates p53 functions by activation of HIPK2 kinase through multimeric complex formation
Abstract
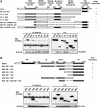
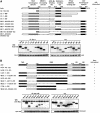
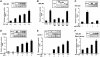
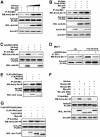
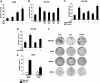
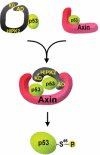
Axin and p53 are tumor suppressors, controlling cell growth, apoptosis, and development. We show that Axin interacts with homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 (HIPK2), which is linked to UV-induced p53-dependent apoptosis by interacting with, and phosphorylating Ser 46 of, p53. In addition to association with p53 via HIPK2, Axin contains a separate domain that directly interacts with p53 at their physiological concentrations. Axin stimulates p53-dependent reporter transcription in 293 cells, but not in 293T, H1299, or SaOS-2 cells that are defective in p53 signaling. Axin, but not AxindeltaHIPK2, activates HIPK2-mediated p53 phosphorylation at Ser 46, facilitating p53-dependent transcriptional activity and apoptosis. Specific knockdown of Axin by siRNA reduced UV-induced Ser-46 phosphorylation and apoptosis. Kinase-dead HIPK2 reduced Axin-induced p53-dependent transcriptional activity, indicating that Axin stimulates p53 function through HIPK2 kinase activity. Interestingly, HIPK2deltaAxin that lacks its Axin-binding region acts as a dominant-positive form in p53 activation, suggesting that the Axin-binding region of HIPK2 is a putative autoinhibitory domain. These results show that Axin acts as a tumor suppressor by facilitating p53 function through integration of multiple factors.
Figures

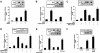
Similar articles
-
Daxx cooperates with the Axin/HIPK2/p53 complex to induce cell death.Cancer Res. 2007 Jan 1;67(1):66-74. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1671. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17210684
-
HIPK2 contributes to PCAF-mediated p53 acetylation and selective transactivation of p21Waf1 after nonapoptotic DNA damage.Oncogene. 2005 Aug 18;24(35):5431-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208717. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15897882
-
Negative regulation of beta4 integrin transcription by homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 and p53 impairs tumor progression.Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 15;69(14):5978-86. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0244. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19567674
-
Regulation of p53 activity by HIPK2: molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications in human cancer cells.Oncogene. 2010 Aug 5;29(31):4378-87. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.183. Epub 2010 May 31. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20514025 Review.
-
Axin bridges Daxx to p53.Cell Res. 2007 Apr;17(4):301-2. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.16. Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17404597 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
DNA damage-induced heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K sumoylation regulates p53 transcriptional activation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 31;287(36):30789-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.390120. Epub 2012 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22825850 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between RUNX1 and AXIN1 in ER-negative versus ER-positive Breast Cancer.Cell Cycle. 2017 Feb 16;16(4):312-318. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1237325. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28055379 Free PMC article.
-
The truncated AXIN1 isoform promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through SRSF9-mediated exon 9 skipping.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):2247-2263. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05012-1. Epub 2024 May 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38748384
-
The Adenoviral E1B-55k Protein Present in HEK293 Cells Mediates Abnormal Accumulation of Key WNT Signaling Proteins in Large Cytoplasmic Aggregates.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 29;12(12):1920. doi: 10.3390/genes12121920. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946869 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress and application of the homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;14(4):373-7. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.04.13. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21496439 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Attardi LD, DePinho RA (2004) Conquering the complexity of p53. Nat Genet 36: 7–8 - PubMed
-
- Brooks CL, Gu W (2003) Ubiquitination, phosphorylation and acetylation: the molecular basis for p53 regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 164–171 - PubMed
-
- Cadigan KM, Nusse R (1997) Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev 11: 3286–3305 - PubMed
-
- Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Maretto S, Insinga A, Imbriano C, Piccolo S (2003) Links between tumor suppressors: p53 is required for TGF-beta gene responses by cooperating with Smads. Cell 113: 301–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

