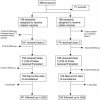
A randomised, double-blind, controlled vaccine efficacy trial of DNA/MVA ME-TRAP against malaria infection in Gambian adults
- PMID: 15526058
- PMCID: PMC524376
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0010033
A randomised, double-blind, controlled vaccine efficacy trial of DNA/MVA ME-TRAP against malaria infection in Gambian adults
Abstract
Background: Many malaria vaccines are currently in development, although very few have been evaluated for efficacy in the field. Plasmodium falciparum multiple epitope (ME)- thrombospondin-related adhesion protein (TRAP) candidate vaccines are designed to potently induce effector T cells and so are a departure from earlier malaria vaccines evaluated in the field in terms of their mechanism of action. ME-TRAP vaccines encode a polyepitope string and the TRAP sporozoite antigen. Two vaccine vectors encoding ME-TRAP, plasmid DNA and modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA), when used sequentially in a prime-boost immunisation regime, induce high frequencies of effector T cells and partial protection, manifest as delay in time to parasitaemia, in a clinical challenge model.
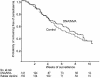
Methods and findings: A total of 372 Gambian men aged 15-45 y were randomised to receive either DNA ME-TRAP followed by MVA ME-TRAP or rabies vaccine (control). Of these men, 296 received three doses of vaccine timed to coincide with the beginning of the transmission season (141 in the DNA/MVA group and 155 in the rabies group) and were followed up. Volunteers were given sulphadoxine/pyrimethamine 2 wk before the final vaccination. Blood smears were collected weekly for 11 wk and whenever a volunteer developed symptoms compatible with malaria during the transmission season. The primary endpoint was time to first infection with asexual P. falciparum. Analysis was per protocol. DNA ME-TRAP and MVA ME-TRAP were safe and well-tolerated. Effector T cell responses to a non-vaccine strain of TRAP were 50-fold higher postvaccination in the malaria vaccine group than in the rabies vaccine group. Vaccine efficacy, adjusted for confounding factors, was 10.3% (95% confidence interval, -22% to +34%; p = 0.49). Incidence of malaria infection decreased with increasing age and was associated with ethnicity.
Conclusions: DNA/MVA heterologous prime-boost vaccination is safe and highly immunogenic for effector T cell induction in a malaria-endemic area. But despite having produced a substantial reduction in liver-stage parasites in challenge studies of non-immune volunteers, this first generation T cell-inducing vaccine was ineffective at reducing the natural infection rate in semi-immune African adults.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mutabingwa T, Nzila A, Mberu E, Nduati E, Winstanley P, et al. Chlorproguanil-dapsone for treatment of drug-resistant falciparum malaria in Tanzania. Lancet. 2001;358:1218–1223. - PubMed
-
- Hemingway J, Field L, Vontas J. An overview of insecticide resistance. Science. 2002;298:96–97. - PubMed
-
- Schofield L, Villaquiran J, Ferreira A, Schellekens H, Nussenzweig R, et al. Gamma interferon, CD8+ T cells and antibodies required for immunity to malaria sporozoites. Nature. 1987;330:664–666. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues MM, Cordey AS, Arreaza G, Corradin G, Romero P, et al. CD8+ cytolytic T cell clones derived against the Plasmodium yoelii circumsporozoite protein protect against malaria. Int Immunol. 1991;3:579–585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical