ESTIMA, a tool for EST management in a multi-project environment
- PMID: 15527510
- PMCID: PMC533868
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-176
ESTIMA, a tool for EST management in a multi-project environment
Abstract
Background: Single-pass, partial sequencing of complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries generates thousands of chromatograms that are processed into high quality expressed sequence tags (ESTs), and then assembled into contigs representative of putative genes. Usually, to be of value, ESTs and contigs must be associated with meaningful annotations, and made available to end-users.
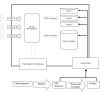
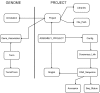
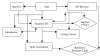
Results: A web application, Expressed Sequence Tag Information Management and Annotation (ESTIMA), has been created to meet the EST annotation and data management requirements of multiple high-throughput EST sequencing projects. It is anchored on individual ESTs and organized around different properties of ESTs including chromatograms, base-calling quality scores, structure of assembled transcripts, and multiple sources of comparison to infer functional annotation, Gene Ontology associations, and cDNA library information. ESTIMA consists of a relational database schema and a set of interactive query interfaces. These are integrated with a suite of web-based tools that allow a user to query and retrieve information. Further, query results are interconnected among the various EST properties. ESTIMA has several unique features. Users may run their own EST processing pipeline, search against preferred reference genomes, and use any clustering and assembly algorithm. The ESTIMA database schema is very flexible and accepts output from any EST processing and assembly pipeline. ESTIMA has been used for the management of EST projects of many species, including honeybee (Apis mellifera), cattle (Bos taurus), songbird (Taeniopygia guttata), corn rootworm (Diabrotica vergifera), catfish (Ictalurus punctatus, Ictalurus furcatus), and apple (Malus x domestica). The entire resource may be downloaded and used as is, or readily adapted to fit the unique needs of other cDNA sequencing projects.
Conclusions: The scripts used to create the ESTIMA interface are freely available to academic users in an archived format from http://titan.biotec.uiuc.edu/ESTIMA/. The entity-relationship (E-R) diagrams and the programs used to generate the Oracle database tables are also available. We have also provided detailed installation instructions and a tutorial at the same website. Presently the chromatograms, EST databases and their annotations have been made available for cattle and honeybee brain EST projects. Non-academic users need to contact the W.M. Keck Center for Functional and Comparative Genomics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, for licensing information.
Figures

Similar articles
-
JUICE: a data management system that facilitates the analysis of large volumes of information in an EST project workflow.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Nov 23;7:513. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-513. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17123449 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken genomics resource: sequencing and annotation of 35,407 ESTs from single and multiple tissue cDNA libraries and CAP3 assembly of a chicken gene index.Physiol Genomics. 2006 May 16;25(3):514-24. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00207.2005. Epub 2006 Mar 22. Physiol Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16554550
-
ESTree db: a tool for peach functional genomics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Dec 1;6 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-S4-S16. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16351742 Free PMC article.
-
A hitchhiker's guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2007 Jan;8(1):6-21. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl015. Epub 2006 May 23. Brief Bioinform. 2007. PMID: 16772268 Review.
-
Rapid in silico cloning of genes using expressed sequence tags (ESTs).Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2000;5:25-44. doi: 10.1016/s1387-2656(00)05031-6. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2000. PMID: 10874996 Review.
Cited by
-
Expressed sequences tags of the anther smut fungus, Microbotryum violaceum, identify mating and pathogenicity genes.BMC Genomics. 2007 Aug 10;8:272. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-272. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17692127 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiological investigation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in Northwest China from 2007 to 2010.Virus Genes. 2012 Aug;45(1):90-7. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0747-4. Epub 2012 Jun 23. Virus Genes. 2012. PMID: 22729801
-
Transcriptome analysis of the desert locust central nervous system: production and annotation of a Schistocerca gregaria EST database.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 21;6(3):e17274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017274. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21445293 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Analysis of the Venom Gland Transcriptomes of the Fishing Spiders Dolomedes mizhoanus and Dolomedes sulfurous.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 7;10(10):e0139908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139908. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26445494 Free PMC article.
-
Design and implementation of a generalized laboratory data model.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Sep 26;8:362. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-362. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17897463 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

