A screen for genes that suppress loss of contact inhibition: identification of ING4 as a candidate tumor suppressor gene in human cancer
- PMID: 15528276
- PMCID: PMC528940
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407158101
A screen for genes that suppress loss of contact inhibition: identification of ING4 as a candidate tumor suppressor gene in human cancer
Abstract
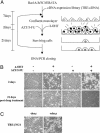
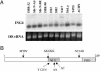
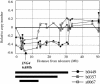
We have devised a screen for genes that suppress the loss of contact inhibition elicited by overexpression of the protooncogene MYCN. The initial application of this screen detected nine distinctive suppressors within a representative human cDNA library. One of these genes was ING4, a potential tumor suppressor gene that maps to human chromosome 12p13. Ectopic expression of ING4 suppressed the loss of contact inhibition elicited by either MYCN or MYC but had no direct effect on cellular proliferation. Pursuing the possibility that ING4 might be a tumor suppressor gene, we found inactivating mutations in ING4 transcripts from various human cancer cell lines. In addition, we used comparative genomic hybridization to detect deletion of the ING4 locus in 10-20% of human breast cancer cell lines and primary breast tumors. Ectopic expression of ING4 attenuated the growth of T47D human breast cancer cells in soft agar. We conclude that ING4 is a strong candidate as a tumor suppressor gene.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Frequent deletion and down-regulation of ING4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at 12p13, in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Gene. 2005 Aug 15;356:109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.02.014. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15935570
-
Adenovirus-mediated ING4/IL-24 double tumor suppressor gene co-transfer enhances antitumor activity in human breast cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 Oct;28(4):1315-24. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1930. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22842937
-
Adenovirus-mediated ING4 Gene Transfer in Osteosarcoma Suppresses Tumor Growth via Induction of Apoptosis and Inhibition of Tumor Angiogenesis.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;14(5):617-26. doi: 10.7785/tcrt.2012.500424. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 24750000
-
HuntING4 new tumor suppressors.Cell Cycle. 2005 Apr;4(4):516-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.4.1584. Epub 2005 Apr 2. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15738650 Review.
-
The essential role of tumor suppressor gene ING4 in various human cancers and non-neoplastic disorders.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jan 30;39(1):BSR20180773. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180773. Print 2019 Jan 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30643005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Circumscribed Exposure to the Pan-Aurora Kinase Inhibitor VX-680 on Proliferating Euploid Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 11;23(20):12104. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012104. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36292957 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of growth tumor suppressors in cancer progression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jun;67(12):1987-99. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0312-z. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20195696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ING gene family in the regulation of cell growth and tumorigenesis.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jan;218(1):45-57. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21583. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18780289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-content screen identifies the vulnerability of MYC-overexpressing cells to dimethylfasudil.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 24;16(3):e0248355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248355. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33760847 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of deleterious passenger mutations on cancer progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 19;110(8):2910-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213968110. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23388632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng, X., Hara, Y. & Riabowol, K. (2002) Trends Cell Biol. 12, 532-538. - PubMed
-
- Aasland, R., Gibson, T. J. & Stewart, A. F. (1995) Trends Biochem. Sci. 20, 56-59. - PubMed
-
- Nagashima, M., Shiseki, M., Pedeux, R. M., Okamura, S., Kitahama-Shiseki, M., Miura, K., Yokota, J. & Harris, C. C. (2003) Oncogene 22, 343-350. - PubMed
-
- Shiseki, M., Nagashima, M., Pedeux, R. M., Kitahama-Shiseki, M., Miura, K., Okamura, S., Onogi, H., Higashimoto, Y., Appella, E., Yokota, J. & Harris, C. C. (2003) Cancer Res. 63, 2373-2378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

