Use of merocyanine 540 for photodynamic inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus planktonic and biofilm cells
- PMID: 15528505
- PMCID: PMC525131
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6453-6458.2004
Use of merocyanine 540 for photodynamic inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus planktonic and biofilm cells
Abstract
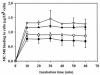
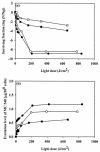
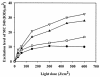
Photodynamic inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus planktonic and biofilm cells by a phtotosensitizer, merocyanine 540 (MC 540), was investigated. For the planktonic experiments, MC 540 binding efficiency to bacterial cells was found to increase with both increasing MC 540 concentration and increasing incubation time, but the binding became saturated following 10 min of incubation. The antimicrobial activity was enhanced with an increasing light dose, but an increase in the light dose could not further improve the antimicrobial activity if the maximum excitation level attainable was less than the necessary minimum threshold level. Complete inactivation was achieved when the excitation level of MC 540 was somewhere above the threshold level. The relationship between antimicrobial activity and the excitation level of MC 540 revealed that the more MC 540 was excited, the more S. aureus cells were killed. For the biofilm experiments, the antimicrobial activity was enhanced with an increase in the light dose. No viable cells were detected when organisms were exposed to 15 mug of MC 540 per ml and a light dose of 600 J/cm2 or to 20 mug of MC 540 per ml and a light dose of 450 J/cm2. A quantitative analysis of MC 540 bound to biofilms was also performed, and the images from confocal laser scanning microscopy provided direct evidence that revealed the difference between the MC 540 remaining in the biofilms prior to irradiation and the MC 540 remaining in the biofilms after irradiation. The results of both the planktonic and biofilm experiments suggest that the antimicrobial activity of photodynamic inactivation of S. aureus is closely related to the excitation level of MC 540.
Figures


References
-
- Ackroyd, R., C. Kelty, N. Brown, and M. Reed. 2001. The history of photodetection and photodynamic therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 74:656-669. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Hur, E., R. C. Hoeben, H. Van Ormondt, T. M. Dubbelman, and J. Van Steveninck. 1992. Photodynamic inactivation of retroviruses by phthalocyanines: the effects of sulphonation, metal ligand and fluoride. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 13:145-152. - PubMed
-
- Carre, V., O. Gaud, I. Sylvain, O. Bourdon, M. Spiro, J. Blais, R. Granet, P. Krausz, and M. Guilloton. 1999. Fungicidal properties of meso-arylglycosylporphyrins: influence of sugar substituents on photoinduced damage in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 48:57-62. - PubMed
-
- Costerton, J. W., Z. Lewandowski, D. E. Caldwell, D. R. Korber, and H. M. Lappin-Scott. 1995. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 49:711-745. - PubMed
-
- Coudron, P. E., and C. W. Stratton. 1995. Utilization of time-kill kinetic methodologies for assessing the bactericidal activities of ampicillin and bismuth, alone and in combination, against Helicobacter pylori in stationary and logarithmic growth phases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39:66-69. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

