Display of biologically functional insecticidal toxin on the surface of lambda phage
- PMID: 15528522
- PMCID: PMC525175
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6587-6594.2004
Display of biologically functional insecticidal toxin on the surface of lambda phage
Abstract
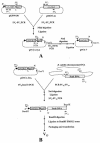
The successful use of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins to control agricultural pests could be undermined by the evolution of insect resistance. Under selection pressure in the laboratory, a number of insects have gained resistance to the toxins, and several cases of resistance in the diamondback moth have been reported from the field. The use of protein engineering to develop novel toxins active against resistant insects could offer a solution to this problem. The display of proteins on the surface of phages has been shown to be a powerful technology to search for proteins with new characteristics from combinatorial libraries. However, this potential of phage display to develop Cry toxins with new binding properties and new target specificities has hitherto not been realized because of the failure of displayed Cry toxins to bind their natural receptors. In this work we describe the construction of a display system in which the Cry1Ac toxin is fused to the amino terminus of the capsid protein D of bacteriophage lambda. The resultant phage was viable and infectious, and the displayed toxin interacted successfully with its natural receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Bell, R. A., and F. G. Joachim. 1976. Techniques for rearing laboratory colonies of tobacco hornworms and pink bollworms. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 69:365-373.
-
- Blattner, F. R., A. E. Blechl, K. Denniston-Thompson, H. E. Faber, J. E. Richards, J. L. Slightom, P. W. Tucker, and O. Smithies. 1978. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science 202:1279-1284. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Burton, S. L., D. J. Ellar, J. Li, and D. J. Derbyshire. 1999. N-acetylgalactosamine on the putative insect receptor aminopeptidase-N is recognised by a site on the domain III lectin-like fold of a Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxin. J. Mol. Biol. 287:1011-1022. - PubMed
-
- Carroll, J., and D. J. Ellar. 1993. An analysis of Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin action on insect midgut-membrane permeability using a light scattering assay. Eur. J. Biochem. 214:771-778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

