Real-time PCR for detection and quantification of the protistan parasite Perkinsus marinus in environmental waters
- PMID: 15528525
- PMCID: PMC525192
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6611-6618.2004
Real-time PCR for detection and quantification of the protistan parasite Perkinsus marinus in environmental waters
Abstract
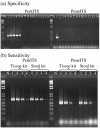
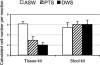
The protistan parasite Perkinsus marinus is a severe pathogen of the oyster Crassostrea virginica along the east coast of the United States. Very few data have been collected, however, on the abundance of the parasite in environmental waters, limiting our understanding of P. marinus transmission dynamics. Real-time PCR assays with SybrGreen I as a label for detection were developed in this study for quantification of P. marinus in environmental waters with P. marinus species-specific primers and of Perkinsus spp. with Perkinsus genus-specific primers. Detection of DNA concentrations as low as the equivalent of 3.3 x 10(-2) cell per 10-microl reaction mixture was obtained by targeting the multicopy internal transcribed spacer region of the genome. To obtain reliable target quantification from environmental water samples, removal of PCR inhibitors and efficient DNA recovery were two major concerns. A DNA extraction kit designed for tissues and another designed for stool samples were tested on environmental and artificial seawater (ASW) samples spiked with P. marinus cultured cells. The stool kit was significantly more efficient than the tissue kit at removing inhibitors from environmental water samples. With the stool kit, no significant difference in the quantified target concentrations was observed between the environmental and ASW samples. However, with the spiked ASW samples, the tissue kit demonstrated more efficient DNA recovery. Finally, by performing three elutions of DNA from the spin columns, which were combined prior to target quantification, variability of DNA recovery from different samples was minimized and more reliable real-time PCR quantification was accomplished.
Figures
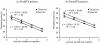
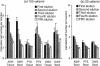
References
-
- Andrews, J. D. 1988. Epizootiology of the disease caused by the oyster pathogen Perkinsus marinus and its effect on the oyster industry. Am. Fish. Soc. Spec. Publ. 18:47-63.
-
- Bach, H.-J., J. Tomanova, M. Scholter, and J. C. Munch. 2002. Enumeration of total bacteria with genes for proteolytic activity in pure cultures and in environmental samples by quantitative PCR mediated amplification. J. Microbiol. Methods 49:235-245. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A. B., and L. C. Ranford-Cartwright. 2002. Real-time quantitative PCR in parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 18:337-342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

