Novel sulfonolipid in the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber
- PMID: 15528534
- PMCID: PMC525256
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6678-6685.2004
Novel sulfonolipid in the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber
Abstract
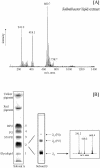
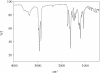
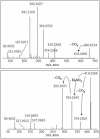
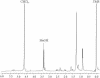
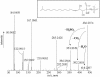
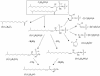
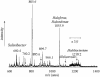
Salinibacter ruber is an extremely halophilic bacterium, phylogenetically affiliated with the Flavobacterium/Cytophaga branch of the domain Bacteria. Electrospray mass analyses (negative ion) of the total lipid extract of a pure culture of S. ruber shows a characteristic peak at m/z 660 as the most prominent peak in the high-mass range of the spectrum. A novel sulfonolipid, giving rise to the molecular ion [M-H]- of m/z 660, has been identified. The sulfonolipid isolated and purified by thin-layer chromatography was shown by chemical degradation, mass spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance analysis to have the structure 2-carboxy-2-amino-3-O-(13'-methyltetradecanoyl)-4-hydroxy-18-methylnonadec-5-ene-1-sulfonic acid. This lipid represents about 10% of total cellular lipids, and it appears to be a structural variant of the sulfonolipids found as main components of the cell envelope of gliding bacteria of the genus Cytophaga and closely related genera (W. Godchaux and E. R. Leadbetter, J. Bacteriol. 153:1238-1246, 1983) and of diatoms (R. Anderson, M. Kates, and B. E. Volcani, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 528:89-106, 1978). Since this sulfonolipid has never been observed in any other extreme halophilic microorganism, we consider the peak at m/z 660 the lipid signature of Salinibacter. This study suggests that this novel sulfonolipid may be used as a chemotaxonomic marker for the detection of Salinibacter within the halophilic microbial community in saltern crystallizer ponds and other hypersaline environments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of polar membrane lipids of the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber and possible role of cardiolipin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1791(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.10.003. Epub 2008 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18996223
-
Glycerol metabolism in the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004 Mar 19;232(2):211-5. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(04)00077-1. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15033241
-
Intracellular ion and organic solute concentrations of the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber.Extremophiles. 2002 Dec;6(6):491-8. doi: 10.1007/s00792-002-0286-3. Epub 2002 Aug 24. Extremophiles. 2002. PMID: 12486458
-
Salinibacter: an extremely halophilic bacterium with archaeal properties.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013 May;342(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12094. Epub 2013 Feb 25. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23373661 Review.
-
Glycosphingolipid structural analysis and glycosphingolipidomics.Methods Enzymol. 2005;405:300-69. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)05012-3. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413319 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Biosynthesis of Pro-Inflammatory Sulfonolipids from an Opportunistic Pathogen Chryseobacterium gleum.ACS Chem Biol. 2022 May 20;17(5):1197-1206. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00141. Epub 2022 Apr 27. ACS Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35476918 Free PMC article.
-
Salty sisters: The women of halophiles.Front Microbiol. 2014 Jun 4;5:192. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00192. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24926287 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Based Taxonomic Classification of Bacteroidetes.Front Microbiol. 2016 Dec 20;7:2003. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02003. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 28066339 Free PMC article.
-
Biodiversity of sphingoid bases ("sphingosines") and related amino alcohols.J Lipid Res. 2008 Aug;49(8):1621-39. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800012-JLR200. Epub 2008 May 21. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18499644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
L-cysteate sulpho-lyase, a widespread pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-coupled desulphonative enzyme purified from Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3(T).Biochem J. 2006 Mar 15;394(Pt 3):657-64. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051311. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16302849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfredsson, G. A., J. K. Kristjansson, S. Hjorleifsdottir, and K. O. Stetter. 1988. Rhodothermus marinus gen. nov., a thermophilic bacterium from submarine hot springs in Iceland. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134:299-306.
-
- Anderson, R., M. Kates, and B. E. Volcani. 1978. Identification of the sulfonolipids in the non-photosynthetic diatom Nitzschia alba. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 528:89-106. - PubMed
-
- Antón, J., A. Oren, S. Benlloch, F. Rodríguez-Valera, R. Amann, and R. Rosselló-Mora. 2002. Salinibacter ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., a new species of extremely halophilic Bacteria from saltern crystallizer ponds. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52:485-491. - PubMed
-
- Batrakov, S. G., A. E. Mosezhnyi, A. O. Ruzhitsky, V. I. Sheichenko, and D. I. Nikitin. 2000. The polar-lipid composition of the sphingolipid-producing bacterium Flectobacillus major. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1484:225-240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

