Role of Cannomys badius as a natural animal host of Penicillium marneffei in India
- PMID: 15528698
- PMCID: PMC525236
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5070-5075.2004
Role of Cannomys badius as a natural animal host of Penicillium marneffei in India
Abstract
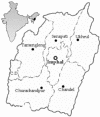
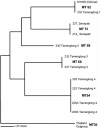
Infection by Penicillium marneffei in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients in India has recently been described; the aim of our study was to survey wild rodents and their associated environment in order to identify the natural populations of this fungus. Surveys recovered P. marneffei from the internal organs of 10 (9.1%) of 110 bamboo rats (Cannomys badius) examined from Manipur state, India, an area endemic for penicilliosis marneffei. Identification of the isolates was based on a detailed study of their morphological characteristics, in vitro conversion to fission yeast form, and exoantigen tests. Multilocus microsatellite typing (MLMT) of the isolates revealed five genotypes. No genotypes were shared between sample sites, and all bamboo rats were infected with a single genotype within sample sites, demonstrating spatial genetic heterogeneity. One MLMT genotype was identical to that seen in a human isolate, suggesting that either coinfection from a common source or host-to-host transmission had occurred. This demonstrates the utility of an MLMT-based approach to elucidating the epidemiology of P. marneffei.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Common reservoirs for Penicillium marneffei infection in humans and rodents, China.Emerg Infect Dis. 2011 Feb;17(2):209-14. doi: 10.3201/eid1702.100718. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21291590 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Penicillium marneffei infections among wild bamboo rats in Thailand.Mycopathologia. 1995 Jul;131(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01103897. Mycopathologia. 1995. PMID: 8532047
-
Penicillium marneffei--an indicator disease of AIDS: a case report.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2007 Jul;50(3):674-6. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17883182
-
Penicillium marneffei infection and recent advances in the epidemiology and molecular biology aspects.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jan;19(1):95-110. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.95-110.2006. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16418525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infection due to Penicillium marneffei, an emerging pathogen: review of 155 reported cases.Clin Infect Dis. 1996 Jul;23(1):125-30. doi: 10.1093/clinids/23.1.125. Clin Infect Dis. 1996. PMID: 8816141 Review.
Cited by
-
Common reservoirs for Penicillium marneffei infection in humans and rodents, China.Emerg Infect Dis. 2011 Feb;17(2):209-14. doi: 10.3201/eid1702.100718. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21291590 Free PMC article.
-
Sixty Years from Segretain's Description: What Have We Learned and Should Learn About the Basic Mycology of Talaromyces marneffei?Mycopathologia. 2019 Dec;184(6):721-729. doi: 10.1007/s11046-019-00395-y. Mycopathologia. 2019. PMID: 31599369
-
Penicillium marneffei Infection in AIDS.Patholog Res Int. 2011 Feb 10;2011:764293. doi: 10.4061/2011/764293. Patholog Res Int. 2011. PMID: 21331327 Free PMC article.
-
Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei infection in non-HIV-infected patients.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016 Mar 9;5(3):e19. doi: 10.1038/emi.2016.18. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 26956447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Talaromyces marneffei Yeasts Mediate Inflammatory Response in Macrophage Cells by Bioactive Protein Components.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 8;11:603183. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.603183. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33488545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajello, L., A. A. Padhye, S. Sukroongreung, C. H. Nilakul, and S. Tantimavanic. 1995. Occurrence of Penicillium marneffei infections among wild bamboo rats in Thailand. Mycopathologia 131:1-8. - PubMed
-
- Beneke, E. S., and A. L. Rogers. 1996. Medical mycology and human mycoses, p. 40-48. Star Publishing Co., Belmont, Calif
-
- Capponi, M. P., G. Segretain, and G. Sureau. 1956. Penicilliosis de Rhizomys sinensis. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. Filiales 49:418-421. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti, A., N. Nayak, and P. Talwar. 1991. In vitro proteinase production by Candida species. Mycopathologia 114:163-168. - PubMed
-
- Chariyalertsak, S., P. Vanittanakom, K. E. Nelson, T. Sirisanthana, and N. Vanittanakom. 1996. Rhizomys sumatrensis and Cannomys badius, new natural animal hosts of Penicillium marneffei. J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 34:105-110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

