Mapping of antigenic sites on the nucleocapsid protein of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID: 15528730
- PMCID: PMC525273
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5309-5314.2004
Mapping of antigenic sites on the nucleocapsid protein of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
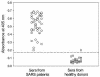
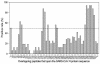
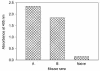
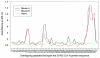
Antigenic sites on the nucleocapsid (N) protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus (SARS-CoV) were mapped by Pepscan analysis with overlapping peptides that span the N protein sequence. Two major immunodominant epitopes located in the C-terminal region (amino acids [aa] 362 to 412) and middle region (aa 153 to 178) reacted with more than 75% of sera from SARS patients. Several minor immunodominant epitopes were reactive with about 50% of the SARS sera. Antisera from mice immunized with inactivated SARS-CoV recognized the two major immunodominant epitopes and one antigenic site located adjacent to the N-terminal region (aa 76 to 101), which did not react with the sera from SARS patients. Several monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV bound to the N- or C-terminal antigenic sites. These results suggest that the above antigenic sites on the N protein are important in eliciting humoral immune response against SARS-CoV in humans and animals and can be used as antigens for developing diagnostic tests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two-way antigenic cross-reactivity between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and group 1 animal CoVs is mediated through an antigenic site in the N-terminal region of the SARS-CoV nucleoprotein.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(24):13365-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01169-07. Epub 2007 Oct 3. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17913799 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immunodominant sites on the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus: implication for developing SARS diagnostics and vaccines.J Immunol. 2004 Sep 15;173(6):4050-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.6.4050. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15356154
-
Immunological characterizations of the nucleocapsid protein based SARS vaccine candidates.Vaccine. 2006 Apr 12;24(16):3100-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.01.058. Epub 2006 Feb 8. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16494977 Free PMC article.
-
Determination and application of immunodominant regions of SARS coronavirus spike and nucleocapsid proteins recognized by sera from different animal species.J Immunol Methods. 2008 Feb 29;331(1-2):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2007.11.009. Epub 2007 Dec 17. J Immunol Methods. 2008. PMID: 18191140 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplicity of uses of monoclonal antibodies that define papillomavirus linear immunodominant epitopes.Immunol Res. 1997 Feb;16(1):115-9. doi: 10.1007/BF02786327. Immunol Res. 1997. PMID: 9048212 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation and characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody specific to severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus nucleocapsid protein.Virus Res. 2006 Dec;122(1-2):109-18. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.07.004. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Virus Res. 2006. PMID: 16942813 Free PMC article.
-
Host DDX Helicases as Possible SARS-CoV-2 Proviral Factors: A Structural Overview of Their Hijacking Through Multiple Viral Proteins.Front Chem. 2020 Dec 10;8:602162. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.602162. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 33381492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Epitopes from Treponema pallidum Lipoprotein Antigens for Syphilis Diagnosis and Treatment Prognosis.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 13;11(6):1606-1622. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5c00155. Epub 2025 May 23. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40407751 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamers targeting SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein exhibit potential anti pan-coronavirus activity.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Feb 14;9(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01748-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38355661 Free PMC article.
-
Immunodominant SARS Coronavirus Epitopes in Humans Elicited both Enhancing and Neutralizing Effects on Infection in Non-human Primates.ACS Infect Dis. 2016 May 13;2(5):361-76. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.6b00006. Epub 2016 Apr 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27627203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casal, J. I., M. J. Rodriguez, J. Sarraseca, J. Garcia, J. Plana-Duran, and A. Sanz. 1998. Identification of a common antigenic site in the nucleocapsid protein of European and North American isolates of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 440:469-477. - PubMed
-
- Drosten, C., S. Gunther, W. Preiser, S. van derWerf H. R. Brodt, S. Becker, H. Rabenau, M. Panning, L. Kolesnikova, R. A. Fouchier, A. Berger, A. M. Burguiere, J. Cinatl, M. Eickmann, N. Escriou, K. Grywna, S. Kramme, J. C. Manuguerra, S. Muller, V. Rickerts, M. Sturmer, S. Vieth, H. D. Klenk, A. D. Osterhaus, H. Schmitz, and H. W. Doerr. 2003. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1967-1976. - PubMed
-
- Ignjatovic, J., and L. Galli. 1993. Structural proteins of avian infectious bronchitis virus: role in immunity and protection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 342:449-453. - PubMed
-
- Kim, T. W., J. H. Lee, C. F. Hung, S. Peng, R. Roden, M. C. Wang, R. Viscidi, Y. C. Tsai, L. He, P. J. Chen, D. A. Boyd, and T. C. Wu. 2004. Generation and characterization of DNA vaccines targeting the nucleocapsid protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 78:4638-4645. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

