Chemical approaches to controlling intracellular protein degradation
- PMID: 15532104
- PMCID: PMC2556563
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.200400274
Chemical approaches to controlling intracellular protein degradation
Figures
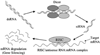

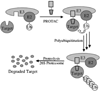
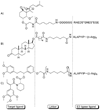

References
-
- Harvey DM, Caskey CT. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1998;2:512. - PubMed
-
- Dwek MV, Brooks SA. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2004;4:425. - PubMed
-
- Bishop AC, Buzko O, Shokat KM. Trends Cell. Biol. 2001;11:167. - PubMed
-
- Shokat K, Velleca M. Drug Discovery Today. 2002;7:872. - PubMed
-
- Adams J. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2002;14:628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

