Effect of dietary palm olein oil on oxidative stress associated with ischemic-reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart
- PMID: 15535879
- PMCID: PMC535348
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-4-29
Effect of dietary palm olein oil on oxidative stress associated with ischemic-reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart
Abstract
Background: Palm olein oil (PO), obtained from refining of palm oil is rich in monounsaturated fatty acid and antioxidant vitamins and is widely used as oil in diet in many parts of the world including India. Palm oil has been reported to have beneficial effects in oxidative stress associated with hypertension and arterial thrombosis. Oxidative stress plays a major role in the etiopathology of myocardial ischemic-reperfusion injury (IRI) which is a common sequel of ischemic heart disease. Antioxidants have potent therapeutic effects on both ischemic heart disease and ischemic-reperfusion injury. Information on the effect of PO on ischemic-reperfusion injury is, however, lacking. In the present study, the effect of dietary palm olein oil on oxidative stress associated with IRI was investigated in an isolated rat heart model. Wistar rats (150-200 gm) of either sex were divided into three different groups (n = 16). Rats were fed with palm olein oil supplemented commercial rat diet, in two different doses [5% v / w (PO 5) and 10% v / w (PO 10) of diet] for 30 days. Control rats (C) were fed with normal diet. After 30 days, half the rats from each group were subjected to in vitro myocardial IRI (20 min of global ischemia, followed by 40 min of reperfusion). Hearts from all the groups were then processed for biochemical and histopathological studies. One way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test was applied to test for significance and values are expressed as mean +/- SE (p < 0.05).
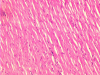
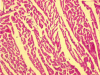
Results: There was a significant increase in myocardial catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities with no significant change in myocardial thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) only in group PO 5 as compared to group C. There was no light microscopic evidence of tissue injury. A significant rise in myocardial TBARS and depletion of myocardial endogenous antioxidants (SOD, CAT and GPx) along with significant myocyte injury was observed in control rats subjected to ischemia-reperfusion (C IR). Hearts from palm olein oil fed rats subjected to ischemia-reperfusion (PO 5 IR and PO 10 IR) were protected from increase in TBARS and depletion of endogenous antioxidants as compared to C IR group. No significant myocyte injury was present in the treated groups.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated for the first time that dietary palm olein oil protected rat heart from oxidative stress associated with ischemic-reperfusion injury.
Figures


References
-
- Braunwald E, Kloner RA. The stunned myocardium: Prolonged post ischemic ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 1982;66:1146–1148. - PubMed
-
- Hemnami T, Parihar MS. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative DNA damage. Ind J Pharm. 1998;48:410–452.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

