Characterization of a novel ATR-dependent, Chk1-independent, intra-S-phase checkpoint that suppresses initiation of replication in Xenopus
- PMID: 15536124
- PMCID: PMC2701543
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.01400
Characterization of a novel ATR-dependent, Chk1-independent, intra-S-phase checkpoint that suppresses initiation of replication in Xenopus
Abstract
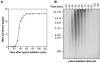
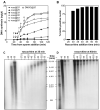
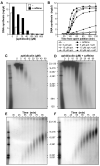
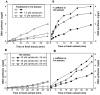
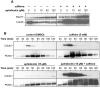
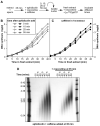
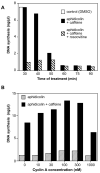
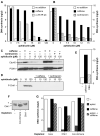
In most eukaryotes, replication origins fire asynchronously throughout S-phase according to a precise timing programme. When replication fork progression is inhibited, an intra-S-phase checkpoint is activated that blocks further origin firing and stabilizes existing replication forks to prevent them undergoing irreversible collapse. We show that chromatin incubated in Xenopus egg extracts displays a replication-timing programme in which firing of new replication origins during S phase depends on the continued activity of S-phase-inducing cyclin-dependent kinases. We also show that low concentrations of the DNA-polymerase inhibitor aphidicolin, which only slightly slows replication-fork progression, strongly suppress further initiation events. This intra-S-phase checkpoint can be overcome by caffeine, an inhibitor of the ATM/ATR checkpoint kinases, or by neutralizing antibodies to ATR. However, depletion or inhibition of Chk1 did not abolish the checkpoint. We could detect no significant effect on fork stability when this intra-S-phase checkpoint was inhibited. Interestingly, although caffeine could prevent the checkpoint from being activated, it could not rescue replication if added after the timing programme would normally have been executed. This suggests that special mechanisms might be necessary to reverse the effects of the intra-S-phase checkpoint once it has acted on particular origins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of replication origin density and firing time in Xenopus egg extracts: role of a caffeine-sensitive, ATR-dependent checkpoint.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 2;279(27):28071-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401574200. Epub 2004 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15123715
-
Xenopus ATR is a replication-dependent chromatin-binding protein required for the DNA replication checkpoint.Curr Biol. 2000 Dec 14-28;10(24):1565-73. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00855-1. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 11137007
-
Chk1 inhibits replication factory activation but allows dormant origin firing in existing factories.J Cell Biol. 2010 Dec 27;191(7):1285-97. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201007074. Epub 2010 Dec 20. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21173116 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that the ATR/Chk1 pathway maintains normal replication fork progression during unperturbed S phase.Cell Cycle. 2006 Oct;5(19):2203-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.19.3256. Epub 2006 Oct 1. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16969104 Review.
-
Replication checkpoint: preventing mitotic catastrophe.Curr Biol. 2001 Feb 20;11(4):R121-4. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00057-4. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11250164 Review.
Cited by
-
Continued primer synthesis at stalled replication forks contributes to checkpoint activation.J Cell Biol. 2010 Apr 19;189(2):233-46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200909105. Epub 2010 Apr 12. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20385778 Free PMC article.
-
The human oncoprotein MDM2 induces replication stress eliciting early intra-S-phase checkpoint response and inhibition of DNA replication origin firing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(2):926-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt944. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24163099 Free PMC article.
-
Open sesame: activating dormant replication origins in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain (Igh) locus.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;23(3):284-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.04.004. Epub 2011 May 14. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21571518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surviving chromosome replication: the many roles of the S-phase checkpoint pathway.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011 Dec 27;366(1584):3554-61. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0071. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22084382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A patient-derived-xenograft platform to study BRCA-deficient ovarian cancers.JCI Insight. 2017 Jan 12;2(1):e89760. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89760. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28097235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blasina A, Price BD, Turenne GA, McGowan CH. Caffeine inhibits the checkpoint kinase ATM. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:1135–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

