Case studies in hypertension: presentation with vaginal bleeding and hypertension
- PMID: 15538100
- PMCID: PMC8109514
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2004.03839.x
Case studies in hypertension: presentation with vaginal bleeding and hypertension
Figures
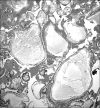


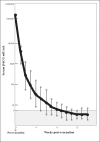
References
-
- ACOG Practice Bulleting #53 . Diagnosis and treatment of gestational trophoblastic disease. Committee on Practice Bulletins‐Gynecology, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologist. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:1365–1377. - PubMed
-
- Moodley M, Tunky K, Moodley J. Gestational trophoblastic syndrome: an audit of 112 patients. A South African experience. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2003;13:234–239. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz RS, Goldstein DP. Pathogenesis of gestational trophoblastic neoplasms. Pathobiol Annu. 1981;11:391–411. - PubMed
-
- Berek JS, Hacker NF. Gestational trophoblastic neoplasi. In: Berek JA, Hacker JA, eds. Practical Gynecologic Oncology. 3rd ed. New York , NY : Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2000:615–638.
-
- Kajii T, Ohama K. Androgenetic origin of hydatidiform mole. Nature. 1977;268:633–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

