Cardiovascular implications of albuminuria
- PMID: 15538106
- PMCID: PMC8109333
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2004.04234.x
Cardiovascular implications of albuminuria
Abstract
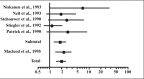
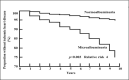
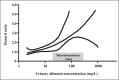
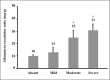
Microalbuminuria is a major independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) events in persons with diabetes or hypertension, the general population, and persons with known CVD. Although microalbuminuria is a stronger risk factor in men, women with increased albuminuria levels are also at a higher risk of CVD. Microalbuminuria is an indicator of generalized endothelial injury, a hallmark of systemic atherosclerosis. Treatments that decrease albuminuria, particularly agents that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system, reduce CVD risk in various populations, including those with and without diabetes or hypertension. Whether albuminuria should be a treatment target for CVD is not yet proven. Nevertheless, the measurement of albuminuria is clinically useful to identify high-risk individuals who should receive intensive risk factor management based on current treatment guidelines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Treat Endocrinol. 2002;1(3):163-73. doi: 10.2165/00024677-200201030-00004. Treat Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 15799209 Review.
-
[Subclinical albuminuria, microalbuminuria and proteinuria--accepted cardiovascular risk markers?].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2006 Nov 24;131(47):2665-71. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-956273. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 17109277 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
Microalbuminuria and cardiovascular disease.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 May;2(3):581-90. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03190906. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17699466 Review.
-
[Microalbuminuria. Signification and value].Presse Med. 1993 Jun 26;22(23):1098-103. Presse Med. 1993. PMID: 8415463 Review. French.
-
New treatment guidelines for a patient with diabetes and hypertension.J Hypertens Suppl. 2003 Mar;21(1):S25-30. J Hypertens Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12769164 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiographic contrast-media-induced acute kidney injury: pathophysiology and prophylactic strategies.ISRN Radiol. 2013 Sep 16;2013:496438. doi: 10.5402/2013/496438. eCollection 2013. ISRN Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24967281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is longitudinal pulse pressure a better predictor of 24-hour urinary albumin excretion than other indices of blood pressure?Hypertension. 2010 Feb;55(2):415-21. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.135087. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20008676 Free PMC article.
-
Albuminuria and Mental Illness Risk: Results From National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2018 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses.Brain Behav. 2025 May;15(5):e70545. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70545. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40350701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity‐onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:356–360. - PubMed
-
- Dinneen SF, Gerstein HC. The association of microalbuminuria and mortality in non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:1413–1418. - PubMed
-
- Jensen JS, Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S, et al. Arterial hypertension, microalbuminuria, and risk of ischemic heart disease. Hypertension. 2000;35:898–903. - PubMed
-
- Hillege HL, Fidler V, Diercks GF, et al. Prevention of Renal and Vascular End Stage Disease (PREVEND) Study Group. Urinary albumin excretion predicts cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality in general population. Circulation. 2002;106:1777–1782. - PubMed
-
- Romundstad S, Holmen J, Kvenild K, et al. Microalbuminuria and all‐cause mortality in 2,089 apparently healthy individuals: a 4.4 year follow‐up study. The Nord‐Trondelag Health Study (HUNT), Norway. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:466–473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

