The E2F family: specific functions and overlapping interests
- PMID: 15538380
- PMCID: PMC535093
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600481
The E2F family: specific functions and overlapping interests
Abstract
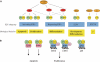
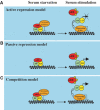
The E2F transcription factors are key regulators of cell cycle progression and the E2F field has made rapid advances since its advent in 1986. Yet, while our understanding of the roles and functions of the E2F family has made enormous progress, with each discovery new questions arise. In this review, we summarise the most recent advances in the field and discuss the remaining key questions. In particular, we will focus on how specificity is achieved among the E2Fs.
Figures

References
-
- Cartwright P, Müller H, Wagener C, Holm K, Helin K (1998) E2F-6: a novel member of the E2F family is an inhibitor of E2F-dependent transcription. Oncogene 17: 611–624 - PubMed
-
- Chellappan S, Hiebert S, Mudryj M, Horowitz J, Nevins J (1991) The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell 65: 1053–1061 - PubMed
-
- Croxton R, Ma Y, Song L, Haura EB, Cress WD (2002) Direct repression of the Mcl-1 promoter by E2F1. Oncogene 21: 1359–1369 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

