Inhibition of oncogenic transformation by mammalian Lin-9, a pRB-associated protein
- PMID: 15538385
- PMCID: PMC533054
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600470
Inhibition of oncogenic transformation by mammalian Lin-9, a pRB-associated protein
Abstract
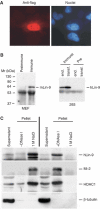
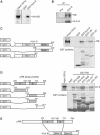
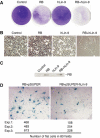
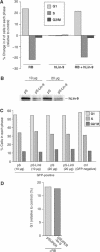
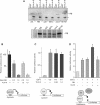
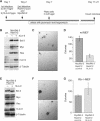
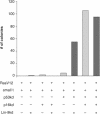
Genetic studies in Caenorhabditis elegans identified lin-9 to function together with the retinoblastoma homologue lin-35 in vulva differentiation. We have now identified a human homologue of Lin-9 (hLin-9) and provide evidence about its function in the mammalian pRB pathway. hLin-9 binds to pRB and cooperates with pRB in flat cell formation in Saos-2 cells. In addition, hLin-9 synergized with pRB and Cbfal to transactivate an osteoblast-specific reporter gene. In contrast, hLin-9 was not involved in pRB-mediated inhibition of cell cycle progression or repression of E2F-dependent transactivation. Consistent with these data, hLin-9 was able to associate with partially penetrant pRB mutants that do not bind to E2F, but retain the ability to activate transcription and to promote differentiation. hLin-9 can also inhibit oncogenic transformation, dependent on the presence of a functional pRB protein. RNAi-mediated knockdown of Lin-9 can substitute for the loss of pRB in transformation of human primary fibroblasts. These data suggest that hLin-9 has tumor-suppressing activities and that the ability of hLin-9 to inhibit transformation is mediated through its association with pRB.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Native E2F/RBF complexes contain Myb-interacting proteins and repress transcription of developmentally controlled E2F target genes.Cell. 2004 Oct 15;119(2):181-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.034. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15479636
-
Conserved region 2 of adenovirus E1A has a function distinct from pRb binding required to prevent cell cycle arrest by p16INK4a or p27Kip1.Oncogene. 2000 Apr 13;19(16):2067-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203534. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10803468
-
The lin-35/Rb and RNAi pathways cooperate to regulate a key cell cycle transition in C. elegans.BMC Dev Biol. 2007 Apr 27;7:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-38. BMC Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17466069 Free PMC article.
-
E2F-Rb complexes regulating transcription of genes important for differentiation and development.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005 Oct;15(5):520-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.07.001. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005. PMID: 16081278 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of E2F-dependent activation and pRB-mediated repression.J Cell Sci. 2004 May 1;117(Pt 11):2173-81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01227. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15126619 Review.
Cited by
-
DYRK1A protein kinase promotes quiescence and senescence through DREAM complex assembly.Genes Dev. 2011 Apr 15;25(8):801-13. doi: 10.1101/gad.2034211. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21498570 Free PMC article.
-
The association of mammalian DREAM complex and HPV16 E7 proteins.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;5(12):3525-33. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26885443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for p38 in transcriptional elongation of p21 (CIP1) in response to Aurora B inhibition.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jul 1;12(13):2051-60. doi: 10.4161/cc.25100. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23759594 Free PMC article.
-
A human tRNA methyltransferase 9-like protein prevents tumour growth by regulating LIN9 and HIF1-α.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Mar;5(3):366-83. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201161. Epub 2013 Feb 4. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23381944 Free PMC article.
-
The human synMuv-like protein LIN-9 is required for transcription of G2/M genes and for entry into mitosis.EMBO J. 2007 Jan 10;26(1):144-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601478. Epub 2006 Dec 7. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17159899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayyar S, Jiang J, Collu A, White-Cooper H, White RA (2003) Drosophila TGIF is essential for developmentally regulated transcription in spermatogenesis. Development 130: 2841–2852 - PubMed
-
- Beitel GJ, Lambie EJ, Horvitz HR (2000) The C. elegans gene lin-9, which acts in an Rb-related pathway, is required for gonadal sheath cell development and encodes a novel protein. Gene 254: 253–263 - PubMed
-
- Bhatt AM, Zhang Q, Harris SA, White-Cooper H, Dickinson H (2004) Gene structure and molecular analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana ALWAYS EARLY homologs. Gene 336: 219–229 - PubMed
-
- Boxem M, van den Heuvel S (2002) C. elegans class B synthetic multivulva genes act in G(1) regulation. Curr Biol 12: 906–911 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R (2002) A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296: 550–553 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

