Depletion of synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis by an anti-FcgammaRI-calicheamicin immunoconjugate
- PMID: 15539412
- PMCID: PMC1755535
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.028845
Depletion of synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis by an anti-FcgammaRI-calicheamicin immunoconjugate
Abstract
Background: Monocytes/macrophages have an important and versatile role in joint inflammation and destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objective: To determine the efficiency of monocyte/macrophage elimination by a new drug conjugated antibody (CD64-calicheamicin (CD64-CaMi)) directed to the high affinity receptor for IgG (FcgammaRI).
Methods: Mononuclear cells from peripheral blood and synovial fluid of patients with RA were cultured in the presence of CD64-CaMi. Cell death of monocytes/macrophages was measured by analysis of phenotypic changes (light scatter patterns, CD14 expression, and FcgammaRI expression) and nuclear DNA fragmentation. The selectivity of CD64-CaMi was checked by using FcgammaRI deficient and FcgammaRI transfected cell lines. In addition, the indirect effect of CD64-CaMi-induced macrophage cell death on arthritogenic T(h1) cell activity was determined.
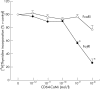
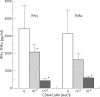
Results: Inflammatory macrophages from RA synovial fluid, expressing increased FcgammaRI levels, were efficiently killed by CD64-CaMi through induction of DNA fragmentation. CD64-CaMi-induced cell death of monocytes/macrophages from peripheral blood of patients with RA proved less efficient. Induction of synovial macrophage death by CD64-CaMi was accompanied by efficient inhibition of proinflammatory T(h1) cytokine production.
Conclusion: Together, the presented data suggest that elimination of macrophages through a new FcgammaRI directed CD64-CaMi is feasible. Because monocytes from peripheral blood are also eliminated by this immunoconjugate, additional experimental studies should validate its potential for local (intra-articular) application in the treatment of RA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selective elimination of synovial inflammatory macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis by an Fcgamma receptor I-directed immunotoxin.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 May;48(5):1229-38. doi: 10.1002/art.10940. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12746896
-
Fcγ receptor profile of monocytes and macrophages from rheumatoid arthritis patients and their response to immune complexes formed with autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jun;70(6):1052-9. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.142091. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21406456
-
CD64-directed immunotoxin inhibits arthritis in a novel CD64 transgenic rat model.J Immunol. 2006 May 15;176(10):5833-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.5833. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16670289
-
B lymphocyte function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: impact of regulatory T lymphocytes and macrophages--modulation by antirheumatic drugs.Dan Med Bull. 1988 Apr;35(2):140-57. Dan Med Bull. 1988. PMID: 3282810 Review.
-
Effector Functions of CD4+ T Cells at the Site of Local Autoimmune Inflammation-Lessons From Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 12;10:353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00353. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30915067 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:708186. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.708186. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34456917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synovial Macrophages: Past Life, Current Situation, and Application in Inflammatory Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 26;13:905356. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.905356. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35958604 Free PMC article.
-
JAB1 determines the response of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts to tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Am J Pathol. 2006 Sep;169(3):889-902. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051161. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16936264 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of CD64 as a marker for the destructive potential of synovitis in osteoarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Apr 2;63(4):1180-1188. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead314. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37341635 Free PMC article.
-
CD64 as novel molecular imaging marker for the characterization of synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Aug 31;25(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03147-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37653557 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

