Inhibition of Wnt/Axin/beta-catenin pathway activity promotes ventral CNS midline tissue to adopt hypothalamic rather than floorplate identity
- PMID: 15539488
- PMCID: PMC2789262
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.01453
Inhibition of Wnt/Axin/beta-catenin pathway activity promotes ventral CNS midline tissue to adopt hypothalamic rather than floorplate identity
Abstract
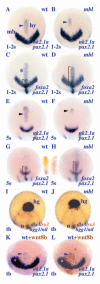
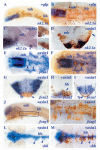
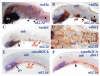
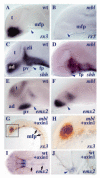
Ventral midline cells in the neural tube form floorplate throughout most of the central nervous system (CNS) but in the anterior forebrain, they differentiate with hypothalamic identity. The signalling pathways responsible for subdivision of midline neural tissue into hypothalamic and floorplate domains are uncertain, and in this study, we have explored the role of the Wnt/Axin/beta-catenin pathway in this process. This pathway has been implicated in anteroposterior regionalisation of the dorsal neural tube but its role in patterning ventral midline tissue has not been rigorously assessed. We find that masterblind zebrafish embryos that carry a mutation in Axin1, an intracellular negative regulator of Wnt pathway activity, show an expansion of prospective floorplate coupled with a reduction of prospective hypothalamic tissue. Complementing this observation, transplantation of cells overexpressing axin1 into the prospective floorplate leads to induction of hypothalamic gene expression and suppression of floorplate marker gene expression. Axin1 is more efficient at inducing hypothalamic markers than several other Wnt pathway antagonists, and we present data suggesting that this may be due to an ability to promote Nodal signalling in addition to suppressing Wnt activity. Indeed, extracellular Wnt antagonists can promote hypothalamic gene expression when co-expressed with a modified form of Madh2 that activates Nodal signalling. These results suggest that Nodal signalling promotes the ability of cells to incorporate into ventral midline tissue, and within this tissue, antagonism of Wnt signalling promotes the acquisition of hypothalamic identity. Wnt signalling also affects patterning within the hypothalamus, suggesting that this pathway is involved in both the initial anteroposterior subdivision of ventral CNS midline fates and in the subsequent regionalisation of the hypothalamus. We suggest that by regulating the response of midline cells to signals that induce ventral fates, Axin1 and other modulators of Wnt pathway activity provide a mechanism by which cells can integrate dorsoventral and anteroposterior patterning information.
Figures

References
-
- Agathon A, Thisse C, Thisse B. The molecular nature of the zebrafish tail organizer. Nature. 2003;424:448–452. - PubMed
-
- Amacher SL, Draper BW, Summers BR, Kimmel CB. The zebrafish T-box genes no tail and spadetail are required for development of trunk and tail mesoderm and medial floor plate. Development. 2002;129:3311–3323. - PubMed
-
- Barth KA, Wilson SW. Expression of zebrafish nk2.2 is influenced by sonic hedgehog/vertebrate hedgehog-1 and demarcates a zone of neuronal differentiation in the embryonic forebrain. Development. 1995;121:1755–1768. - PubMed
-
- Barth KA, Kishimoto Y, Rohr K, Seydler C, Schulte-Merker S, Wilson SW. Bmp activity establishes a gradient of positional information throughout the entire neural plate. Development. 1999;126:4977–4987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

