Apolipoprotein A-I infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue: a control mechanism of cytokine production?
- PMID: 15540281
- PMCID: PMC1064871
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1443
Apolipoprotein A-I infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue: a control mechanism of cytokine production?
Abstract
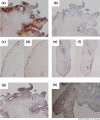
The production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) by monocytes is strongly induced by direct contact with stimulated T lymphocytes, and this mechanism may be critical in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) blocks contact-mediated activation of monocytes, causing inhibition of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta production. This study examined the hypothesis that apoA-I may have a regulatory role at sites of macrophage activation by T lymphocytes in inflamed RA synovial tissue. Synovial tissue samples were obtained after arthroscopy from patients with early untreated RA or treated RA and from normal subjects. As determined by immunohistochemistry, apoA-I was consistently present in inflamed synovial tissue that contained infiltrating T cells and macrophages, but it was absent from noninflamed tissue samples obtained from treated patients and from normal subjects. ApoA-I staining was abundant in the perivascular areas and extended in a halo-like pattern to the surrounding cellular infiltrate. C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A were not detected in the same perivascular areas of inflamed tissues. The abundant presence of apoA-I in the perivascular cellular infiltrates of inflamed RA synovial tissue extends the observations in vitro that showed that apoA-I can modify contact-mediated macrophage production of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. ApoA-I was not present in synovium from patients in apparent remission, suggesting that it has a specific role during phases of disease activity. These findings support the suggestion that the biologic properties of apoA-I, about which knowledge is newly emerging, include anti-inflammatory activities and therefore have important implications for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mast cell activation and its relation to proinflammatory cytokine production in the rheumatoid lesion.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):65-74. doi: 10.1186/ar70. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219391 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of cathepsins K and S expression within the rheumatoid and osteoarthritic synovium.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):663-74. doi: 10.1002/art.10114. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 11920402
-
Interleukin-18 enhances monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1beta production induced by direct contact with T lymphocytes: implications in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Feb;50(2):432-43. doi: 10.1002/art.20064. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 14872485
-
[Rheumatoid arthritis: new developments in the pathogenesis with special reference to synovial fibroblasts].Z Rheumatol. 2001 Oct;60(5):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s003930170030. Z Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11759230 Review. German.
-
Macrophages, synovial tissue and rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993 May-Jun;11(3):331-9. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993. PMID: 8394794 Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-specific proteins from rheumatoid arthritis patients.J Korean Med Sci. 2006 Jun;21(3):478-84. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.478. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. PMID: 16778393 Free PMC article.
-
Protective molecules--C-reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid P (SAP), pentraxin3 (PTX3), mannose-binding lectin (MBL), and apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A1), and their autoantibodies: prevalence and clinical significance in autoimmunity.J Clin Immunol. 2005 Nov;25(6):582-91. doi: 10.1007/s10875-005-7828-2. J Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16380821 Review.
-
The contact-mediated response of peripheral-blood monocytes to preactivated T cells is suppressed by serum factors in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(6):R1189-99. doi: 10.1186/ar1804. Epub 2005 Aug 17. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 16277671 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial fluid proteins differentiate between the subtypes of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Jun;62(6):1813-23. doi: 10.1002/art.27447. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20222116 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I exerts bactericidal activity against Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38211-38219. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.249482. Epub 2011 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21896489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burger D. Cell contact-mediated signaling of monocytes by stimulated T cells: a major pathway for cytokine induction. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000;11:346–353. - PubMed
-
- Hyka N, Dayer JM, Modoux C, Kohno T, Edwards CK III, Roux-Lombard P, Burger D. Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits the production of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by blocking contact-mediated activation of monocytes by T lymphocytes. Blood. 2001;97:2381–2389. doi: 10.1182/blood.V97.8.2381. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

