Endotoxin and Kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 15540801
- PMCID: PMC6668869
Endotoxin and Kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
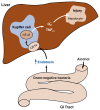
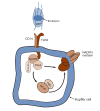
One central component in the complex network of processes leading to the development of alcoholic liver disease is the activation of immune cells residing in the liver (i.e., Kupffer cells) by a substance called endotoxin, which is released by bacteria living in the intestine. Alcohol consumption can lead to increased endotoxin levels in the blood and liver. When activated, Kupffer cells produce signaling molecules (i.e., cytokines) that promote inflammatory reactions as well as molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage liver cells. Endotoxin activates Kupffer cells by interacting with a complex of protein molecules that are located on the outside of the Kupffer cell or which extend into the cell. Binding of endotoxin alters the activities of the proteins in this complex so that they trigger a cascade of biochemical signals in the Kupffer cell, resulting in cytokine and ROS production and, ultimately, liver damage. Because alcohol can enhance endotoxin release and, therefore, Kupffer cell activation, novel approaches to inhibit these processes might help prevent or ameliorate alcoholic liver disease.
Figures
References
-
- Adachi Y, Bradford BU, Gao W, et al. Inactivation of Kupffer cells prevents early alcohol-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 1994;20:453–460. - PubMed
-
- Adachi Y, Moore LE, Bradford BU, et al. Antibiotics prevent liver injury following chronic exposure of rats to ethanol. In: Wisse E, Knook DL, Wake K, editors. Cells of the Hepatic Sinusoid. Leiden, The Netherlands: Kupffer Cell Foundation; 1995. pp. 72–74.
-
- Antal-Szalmas P. Evaluation of CD14 in host defence. European Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2000;30:167–179. - PubMed
-
- Arteel GE, Uesugi T, Bevan LN, et al. Green tea extract protects against early alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. Biological Chemistry. 2002;383:663–670. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Rietschel ET. Innate immune sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2003;3:169–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
