Endoluminal gastroplication in children with significant gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 15542508
- PMCID: PMC1774311
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.041921
Endoluminal gastroplication in children with significant gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
Aims: To describe paediatric experience, and to assess complications and therapeutic effectiveness of the use of endoluminal gastroplication in children with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) refractory to, or dependent on, proton pump inhibitors.
Methods: Seventeen (five male) consecutive children/adolescents (median (range) age 12.4 (6.1-15.9) years, median (range) weight 46.0 (16.5-87.5) kg) with GORD either dependent for more than 12 months on proton pump inhibitors or non-responsive to medical treatment underwent endoscopic gastroplication using a flexible endoscopic sewing device (EndoCinch). Three plications were placed in gastric tissue below the lower oesophageal sphincter. Drug dose requirement, pH measurements, daily symptom severity and frequency, and validated reflux (QOLRAD) and general gastrointestinal (GSRS) quality of life scores were compared before and after endoscopic gastroplication.
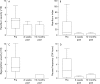
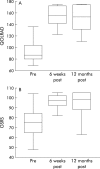
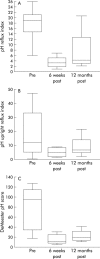
Results: All patients showed post-treatment improvement in symptom severity, frequency, and quality of life scores (p<0.0001). Three patients with recurrent symptomatic GORD had a repeat procedure within six weeks and did well subsequently. At up to 33 months of follow up (median 23), 14/17 patients remained off all antireflux medications, and 14/17 had maintained their symptomatic improvement. All pH parameters improved and had returned to normal values in 14/16 patients post-treatment and in 6/9 after one year of follow-up: in particular the reflux index had decreased from a median of 16.6% (0.9-67%) to 2.5% (0.7-15.7%) (p<0.0001) six weeks and 4.3% (2.2-20.6) (p<0.02) 12 months post-procedure. The only complication observed was gastric bleeding in one patient due to previously undiagnosed coagulopathy, which spontaneously resolved.
Conclusions: Endoluminal gastroplication is an effective and safe procedure in children/adolescents with significant GORD refractory to, or dependent on, medical anti-GORD therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medium-term outcome of endoluminal gastroplication with the EndoCinch device in children.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008 Feb;46(2):172-7. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31814d4de1. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18223376
-
Use of an endoscopic suturing device (the "ESD") to treat patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease, after unsuccessful EndoCinch endoluminal gastroplication: another failure.Endoscopy. 2005 Aug;37(8):700-5. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-870128. Endoscopy. 2005. PMID: 16032486
-
Long term failure of endoscopic gastroplication (EndoCinch).Gut. 2005 Jun;54(6):752-8. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.058354. Gut. 2005. PMID: 15888777 Free PMC article.
-
Review article: The endoscopic treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Dec;26 Suppl 2:1-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03473.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 18081642 Review.
-
Review article: alternative approaches to the long-term management of GERD.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Dec;22 Suppl 3:39-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02711.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16303036 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and new technologies in adult endoscopy: can they be adapted to pediatrics?Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2007 Jun;9(3):208-13. doi: 10.1007/s11894-007-0020-5. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2007. PMID: 17511918 Review.
-
Oats in the diet of children with celiac disease: preliminary results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter Italian study.Nutrients. 2013 Nov 20;5(11):4653-64. doi: 10.3390/nu5114653. Nutrients. 2013. PMID: 24264227 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Mar;66(3):516-554. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001889. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29470322 Free PMC article.
-
Endoluminal and transluminal surgery: current status and future possibilities.Surg Endosc. 2006 Aug;20(8):1179-92. doi: 10.1007/s00464-005-0711-7. Epub 2006 Jul 24. Surg Endosc. 2006. PMID: 16865615 Review.
-
Bone Mineral Density in Boys Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Case-Control Study.J Autism Dev Disord. 2017 Nov;47(11):3608-3619. doi: 10.1007/s10803-017-3277-z. J Autism Dev Disord. 2017. PMID: 28861640
References
-
- Thomson M . Disorders of the oesophagus and stomach in infants. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 1997;11:547–71. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph CD, Mazur LJ, Liptak GS, et al. Guidelines for evaluation and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children: recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2001;32 (suppl 2) :1–31. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd RW, Wren J, Evans S, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux in children. Clinical profile, course and outcome with active therapy in 126 cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1987;26:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Martin AJ, Pratt N, Kennedy JD, et al. Natural history and familial relationships of infant spilling to 9 years of age. Pediatrics 2002;109:1061–7. - PubMed
-
- Hyams JS, Ricci A jr, Leichtner AM. Clinical and laboratory correlates of esophagitis in young children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1988;7:52–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
