Evidence for eviction and rapid deposition of histones upon transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 15542822
- PMCID: PMC529037
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.23.10111-10117.2004
Evidence for eviction and rapid deposition of histones upon transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II
Abstract
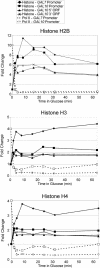
Biochemical experiments indicate that transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is inhibited by nucleosomes and hence requires chromatin-modifying activities. Here, we examine the fate of histones upon passage of elongating Pol II in vivo. Histone density throughout the entire Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL10 coding region is inversely correlated with Pol II association and transcriptional activity, suggesting that the elongating Pol II machinery efficiently evicts core histones from the DNA. Furthermore, new histones appear to be deposited onto DNA less than 1 min after passage of Pol II. Transcription-dependent deposition of histones requires the FACT complex that travels with elongating Pol II. Our results suggest that Pol II transcription generates a highly dynamic equilibrium of histone eviction and histone deposition and that there is significant histone exchange throughout most of the yeast genome within a single cell cycle.
Figures




References
-
- Ahmad, K., and S. Henikoff. 2002. The histone variant H3.3 marks active chromatin by replication-independent nucleosome assembly. Mol. Cell 9:1191-1200. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, O. M., J. V. Geisberg, and K. Struhl. 2004. Chromatin immunoprecipitation for determining the association of proteins with specific genomic sequences in vivo, p. 21.3.1-21.3.17. In F. A. Ausubel, R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.), Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Becker, P. B., and W. Horz. 2002. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:247-273. - PubMed
-
- Belotserkovskaya, R., S. Oh, V. A. Bondarenko, G. Orphanides, V. M. Studitsky, and D. Reinberg. 2003. FACT facilitates transcription-dependent nucleosome alteration. Science 301:1090-1093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
