Human matrix attachment regions are necessary for the establishment but not the maintenance of transgene insulation in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 15542833
- PMCID: PMC529032
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.23.10236-10245.2004
Human matrix attachment regions are necessary for the establishment but not the maintenance of transgene insulation in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
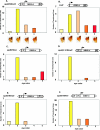
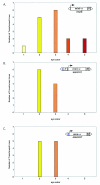
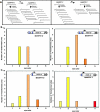
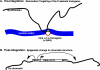
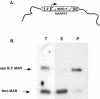
Human matrix attachment regions (MARs) can insulate transgene expression from chromosomal position effects in Drosophila melanogaster. To gain insight into the mechanism(s) by which chromosomal insulation occurs, we studied the expression phenotypes of Drosophila transformants expressing mini-white transgenes in which MAR sequences from the human apoB gene were arranged in a variety of ways. In agreement with previous reports, we found that a single copy of the insulating element was not sufficient for position-independent transgene expression; rather, two copies were required. However, the arrangement of the two elements within the transgene was unimportant, since chromosomal insulation was equally apparent when both copies of the insulator were upstream of the mini-white reporter as when the transcription unit was flanked by insulator elements. Moreover, experiments in which apoB 3' MAR sequences were removed from integrated transgenes in vivo by site-specific recombination demonstrated that MAR sequences were required for the establishment but not for the maintenance of chromosomal insulation. These observations are not compatible with the chromosomal loop model in its simplest form. Alternate mechanisms for MAR function in this system are proposed.
Figures
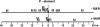
Similar articles
-
Human matrix attachment regions insulate transgene expression from chromosomal position effects in Drosophila melanogaster.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Apr;18(4):2382-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.2382. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9528807 Free PMC article.
-
Position-independent transgene expression mediated by boundary elements from the apolipoprotein B chromatin domain.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):198-207. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.1.198. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7799927 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix attachment region from the chicken lysozyme locus reduces variability in transgene expression and confers copy number-dependence in transgenic rice plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2005 Jun;24(3):145-54. doi: 10.1007/s00299-005-0915-2. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Plant Cell Rep. 2005. PMID: 15714322
-
Evaluation of the function of the human apolipoprotein B gene nuclear matrix association regions in transgenic mice.J Lipid Res. 1996 Oct;37(10):2117-24. J Lipid Res. 1996. PMID: 8906589
-
Sustained transgene expression using MAR elements.Curr Gene Ther. 2008 Oct;8(5):353-66. doi: 10.2174/156652308786071032. Curr Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 18855632 Review.
Cited by
-
New properties of Drosophila scs and scs' insulators.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 24;8(4):e62690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062690. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23638134 Free PMC article.
-
Red flag on the white reporter: a versatile insulator abuts the white gene in Drosophila and is omnipresent in mini-white constructs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Feb;36(3):929-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm992. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18086699 Free PMC article.
-
Evidences for insulator activity of the 5'UTR of the Drosophila melanogaster LTR-retrotransposon ZAM.Mol Genet Genomics. 2010 May;283(5):503-9. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0529-4. Epub 2010 Apr 3. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20364351
-
High-level transgene expression by homologous recombination-mediated gene transfer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Aug;39(15):e104. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr436. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21652640 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse transcription influences can be insulated by the Drosophila SF1 chromatin boundary.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(13):4227-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp362. Epub 2009 May 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19435880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell, A. C., A. G. West, and G. Felsenfeld. 1999. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell 98:387-396. - PubMed
-
- Boulikas, T. 1993. Nature of DNA sequences at the attachment regions of genes to the nuclear matrix. J. Cell. Biochem. 52:14-22. - PubMed
-
- Cai, H. N., and P. Shen. 2001. Effects of cis arrangement of chromatin insulators on enhancer-blocking activity. Science 291:493-495. - PubMed
-
- Chung, J. H., M. Whiteley, and G. Felsenfeld. 1993. A 5′ element of the chicken b-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell 74:505-514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
