Stage-specific repression by the EKLF transcriptional activator
- PMID: 15542849
- PMCID: PMC529052
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.23.10416-10424.2004
Stage-specific repression by the EKLF transcriptional activator
Abstract
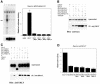
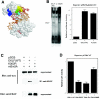
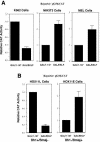
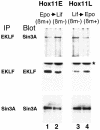
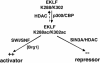
Dynamic changes in transcription factor function can be mediated by switching its interaction with coactivators and corepressors. Erythroid Kruppel-like factor (EKLF) is an erythroid cell-specific transcription factor that plays a critical role in beta-globin gene activation via its interactions with CBP/p300 and SWI/SNF proteins. Unexpectedly, it also interacts with Sin3A and histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) corepressors via its zinc finger domain. We now find that selected point mutants can uncouple activation and repression and that an intact finger structure is not required for interactions with Sin3A/HDAC1 or for transrepression. Most intriguingly, EKLF repression exhibits stage specificity, with reversible EKLF-Sin3A interactions playing a key role in this process. Finally, we have located a key lysine residue that is both a substrate for CBP acetylation and required for Sin3A interaction. These data suggest a model whereby the stage of the erythroid cell alters the acetylation status of EKLF and plays a critical role in directing its coactivator-corepressor interactions and downstream transcriptional effects.
Figures
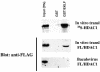
References
-
- Akashi, K., X. He, J. Chen, H. Iwasaki, C. Niu, B. Steenhard, J. Zhang, J. Haug, and L. Li. 2003. Transcriptional accessibility for genes of multiple tissues and hematopoietic lineages is hierarchically controlled during early hematopoiesis. Blood 101:383-389. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, J. A., J. J. Bieker, and B. M. Emerson. 1998. A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1, is required for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell 95:93-104. - PubMed
-
- Barolo, S., and J. W. Posakony. 2002. Three habits of highly effective signaling pathways: principles of transcriptional control by developmental cell signaling. Genes Dev. 16:1167-1181. - PubMed
-
- Bieker, J. J. 2000. EKLF and the development of the erythroid lineage, p. 71-84. In K. Ravid and J. D. Licht (ed.), Transcription factors: normal and malignant development of blood cells. Wiley-Liss, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bieker, J. J. 2001. Kruppel-like factors: three fingers in many pies. J. Biol. Chem. 276:34355-34358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
