Identification of R(-)-isomer of efonidipine as a selective blocker of T-type Ca2+ channels
- PMID: 15545287
- PMCID: PMC1575949
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705944
Identification of R(-)-isomer of efonidipine as a selective blocker of T-type Ca2+ channels
Abstract
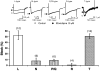
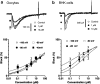
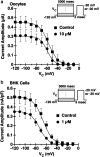
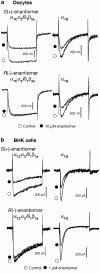
Efonidipine, a derivative of dihydropyridine Ca(2+) antagonist, is known to block both L- and T-type Ca(2+) channels. It remains to be clarified, however, whether efonidipine affects other voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channel subtypes such as N-, P/Q- and R-types, and whether the optical isomers of efonidipine have different selectivities in blocking these Ca(2+) channels, including L- and T-types. To address these issues, the effects of efonidipine and its R(-)- and S(+)-isomers on these Ca(2+) channel subtypes were examined electrophysiologically in the expression systems using Xenopus oocytes and baby hamster kidney cells (BHK tk-ts13). Efonidipine, a mixture of R(-)- and S(+)-isomers, exerted blocking actions on L- and T-types, but no effects on N-, P/Q- and R-type Ca(2+) channels. The selective blocking actions on L- and T-type channels were reproduced by the S(+)-efonidipine isomer. By contrast, the R(-)-efonidipine isomer preferentially blocked T-type channels. The blocking actions of efonidipine and its enantiomers were dependent on holding potentials. These findings indicate that the R(-)-isomer of efonidipine is a specific blocker of the T-type Ca(2+) channel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Five different profiles of dihydropyridines in blocking T-type Ca(2+) channel subtypes (Ca(v)3.1 (alpha(1G)), Ca(v)3.2 (alpha(1H)), and Ca(v)3.3 (alpha(1I))) expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 24;613(1-3):100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.036. Epub 2009 May 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19401195
-
Actions of mibefradil, efonidipine and nifedipine block of recombinant T- and L-type Ca channels with distinct inhibitory mechanisms.Pharmacology. 2006;78(1):11-20. doi: 10.1159/000094900. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Pharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16899990
-
T-type Ca2+ channel blockade prevents sudden death in mice with heart failure.Circulation. 2009 Sep 1;120(9):743-52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.857011. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19687356
-
Efonidipine hydrochloride: a dual blocker of L- and T-type ca(2+) channels.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2002 Winter;20(1):81-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2002.tb00084.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2002. PMID: 12070536 Review.
-
Pathophysiological significance of T-type Ca2+ channels: T-type Ca2+ channels and drug development.J Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Nov;99(3):214-20. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj05002x5. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16293935 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of L- and T-type Ca2+ channels in rat cerebral arteries: role in myogenic tone development.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Jan 1;304(1):H58-71. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00476.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23103495 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic effect of a broad-spectrum dihydropyridine inhibitor of voltage-gated calcium channels.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Dec;467(12):2485-93. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1725-1. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 26286466
-
1,4-dihydropyridines: the multiple personalities of a blockbuster drug family.Transl Med UniSa. 2012 Oct 11;4:12-26. Print 2012 Sep. Transl Med UniSa. 2012. PMID: 23905059 Free PMC article.
-
The transdiagnostic use of worry and rumination to avoid negative emotional contrasts following negative events: A momentary assessment study.J Anxiety Disord. 2023 Apr;95:102679. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2023.102679. Epub 2023 Feb 6. J Anxiety Disord. 2023. PMID: 36863193 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydropyridine-insensitive calcium currents contribute to function of small cerebral arteries.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010 Jun;30(6):1226-39. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.11. Epub 2010 Feb 3. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010. PMID: 20125181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ANDREASEN D., JENSEN B.L., HANSEN P.B., KWON T.H., NIELSEN S., SKOTT O. The alpha(1G)-subunit of a voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channel is localized in rat distal nephron and collecting duct. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2000;279:F997–1005. - PubMed
-
- CRIBBS L.L., GOMORA J.C., DAUD A.N., LEE J.H., PEREZ-REYES E. Molecular cloning and functional expression of Ca(v)3.1c, a T-type calcium channel from human brain. FEBS Lett. 2000;466:54–58. - PubMed
-
- FUJITA Y., MYNLIEFF M., DIRKSEN R.T., KIM M.-S., NIIDOME T., NAKAI J., FRIEDRICH T., IWABE N., MIYATA T., FURUICHI T., FURUTAMA D., MIKOSHIBA K., MORI Y., BEAM K.G. Primary structure and functional expression of the Ω-conotoxin-sensitive N-type calcium channel from rabbit brain. Neuron. 1993;10:585–598. - PubMed
-
- FURUKAWA T., MIURA R., MORI Y., STROBECK M., SUZUKI K., OGIHARA Y., ASANO T., MORISHITA R., HASHII M., HIGASHIDA H., YOSHII M., NUKADA T. Differential interactions of the C treminus and the cytoplasmic I-II loop of neuronal Ca2+ channels with G-protein a and bg subunits II. evidence for direct binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:17595–17603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

