Gestational exposure of Ahr and Arnt hypomorphs to dioxin rescues vascular development
- PMID: 15545609
- PMCID: PMC534507
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404379101
Gestational exposure of Ahr and Arnt hypomorphs to dioxin rescues vascular development
Abstract
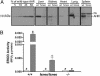
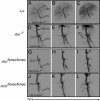
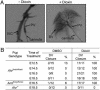
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is commonly known for its role in the adaptive metabolism of xenobiotics and in the toxic events that follow exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (dioxin). Previously, we have demonstrated that the AHR and its heterodimeric partner, the AHR nuclear translocator (ARNT), play a role in the developmental closure of a hepatic vascular shunt known as the ductus venosus (DV). To investigate the mechanism of DV closure, we generated hypomorphic alleles of the Ahr and Arnt loci. Using these models, we then asked whether this vascular defect could be rescued by receptor activation during late development. By manipulating gestational exposure, the patent DV in AHR or ARNT hypomorphs could be efficiently closed by dioxin exposure as early as embryonic day 12.5 and as late as embryonic day 18.5. These findings define the temporal regulation of receptor activation during normal ontogeny and provide evidence to support the idea that receptor activation and AHR-ARNT heterodimerization are essential for normal vascular development. Taken in the broader context, these data demonstrate that similar AHR signaling steps govern all major aspects of AHR biology.
Figures

References
-
- Schmidt, J. V. & Bradfield, C. A. (1996) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 55–89. - PubMed
-
- Whitlock, J. P., Jr., Chichester, C. H., Bedgood, R. M., Okino, S. T., Ko, H. P., Ma, Q., Dong, L., Li, H. & Clarke-Katzenberg, R. (1997) Drug Metab. Rev. 29, 1107–1127. - PubMed
-
- Poland, A. & Knutson, J. C. (1982) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 22, 517–554. - PubMed
-
- Gu, Y.-Z., Hogenesch, J. & Bradfield, C. (2000) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 519–561. - PubMed
-
- Hankinson, O. (1995) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 35, 307–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

