RNA interference using boranophosphate siRNAs: structure-activity relationships
- PMID: 15545637
- PMCID: PMC534620
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh936
RNA interference using boranophosphate siRNAs: structure-activity relationships
Abstract
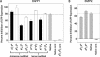
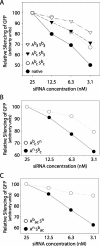
In RNA interference (RNAi), short double-stranded RNA (known as siRNA) inhibits expression from homologous genes. Clinical or pre-clinical use of siRNAs is likely to require stabilizing modifications because of the prevalence of intracellular and extracellular nucleases. In order to examine the effect of modification on siRNA efficacy and stability, we developed a new method for synthesizing stereoregular boranophosphate siRNAs. This work demonstrates that boranophosphate siRNAs are consistently more effective than siRNAs with the widely used phosphorothioate modification. Furthermore, boranophosphate siRNAs are frequently more active than native siRNA if the center of the antisense strand is not modified. Boranophosphate modification also increases siRNA potency. The finding that boranophosphate siRNAs are at least ten times more nuclease resistant than unmodified siRNAs may explain some of the positive effects of boranophosphate modification. The biochemical properties of boranophosphate siRNAs make them promising candidates for an RNAi-based therapeutic.
Figures






Similar articles
-
High potency silencing by single-stranded boranophosphate siRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 22;34(9):2773-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl339. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16717282 Free PMC article.
-
Improving RNA interference in mammalian cells by 4'-thio-modified small interfering RNA (siRNA): effect on siRNA activity and nuclease stability when used in combination with 2'-O-alkyl modifications.J Med Chem. 2006 Mar 9;49(5):1624-34. doi: 10.1021/jm050822c. J Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16509579
-
SiRNAs conjugated with aromatic compounds induce RISC-mediated antisense strand selection and strong gene-silencing activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Oct 5;426(4):571-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.128. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22982308
-
Chemical modification of siRNA.Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009 Dec;Chapter 16:Unit 16.3. doi: 10.1002/0471142700.nc1603s39. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009. PMID: 20013783 Review.
-
Predicting siRNA efficiency.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Jul;64(14):1785-92. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7057-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17415516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted delivery of siRNA.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006;2006(4):63675. doi: 10.1155/JBB/2006/63675. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17057365 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies, design, and chemistry in siRNA delivery systems.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Apr;144:133-147. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 15. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019. PMID: 31102606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of P-Modified DNA from Boranophosphate DNA as a Precursor via Acyl Phosphite Intermediates.J Org Chem. 2023 Aug 4;88(15):10617-10631. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.3c00659. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Org Chem. 2023. PMID: 37462534 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy in Inherited Retinal Diseases: An Update on Current State of the Art.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 15;8:750586. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.750586. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34722588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amides are excellent mimics of phosphate internucleoside linkages and are well tolerated in short interfering RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):6542-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku235. Epub 2014 May 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24813446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denli A.M. and Hannon,G.J. (2003) RNAi: an ever-growing puzzle. Trends Biochem. Sci., 28, 196–201. - PubMed
-
- McManus M.T. and Sharp,P.A. (2002) Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nature Rev. Genet., 3, 737–747. - PubMed
-
- Tuschl T. (2002) Expanding small RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 446–448. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G. and Zamore,P.D. (2002) RNAi: nature abhors a double-strand. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 12, 225–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

