Divergent roles of nitrergic and prostanoid pathways in chronic joint inflammation
- PMID: 15547079
- PMCID: PMC1754842
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.017269
Divergent roles of nitrergic and prostanoid pathways in chronic joint inflammation
Abstract
Background: Nitrergic and prostanoid pathways have both been implicated in inflammatory processes.
Objective: To investigate their respective contributions in a rat model of chronic arthritis.
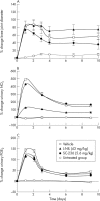
Methods: Male Wistar rats (n = 4-6/group) received either an intra-articular injection of 2% carrageenan/4% kaolin (C/K) or intra- and periarticular injections of Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA; 10 mg/ml M tuberculosis). Joint diameter, urinary nitric oxide metabolites (NO(x)), and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) levels were measured as indices of the inflammatory process. A prophylactic and therapeutic (day 5) dose ranging study of an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, L-N-(1-iminoethyl)-lysine (L-NIL), and a cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, SC-236, was performed with the drugs given subcutaneously. Submaximal doses were identified and used for combination studies. Appropriate vehicle controls were included.
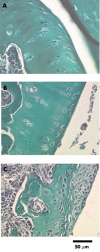
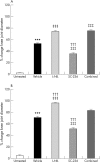
Results: L-NIL and SC-236 dose dependently inhibited C/K induced acute joint swelling, the magnitude being greatest when they were given in combination. Both prophylactic and therapeutic administration of SC-236 in the FCA induced model of chronic arthritis produced a dose dependent reduction in all the measures assessed. However, although L-NIL demonstrated similar dose dependent inhibition of urinary NO(x) and PGE(2) levels, joint swelling was significantly exacerbated in this model. Co-administration of the inhibitors nullified the benefits of SC-236.
Conclusion: Whereas COX-2 derived prostaglandins are proinflammatory in both acute and chronic joint inflammation, NO seems to have divergent roles, being anti-inflammatory in chronic and proinflammatory in acute joint inflammation.
Figures
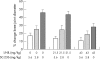

Similar articles
-
Pathophysiology of vascular dysfunction in a rat model of chronic joint inflammation.J Physiol. 2004 Jun 1;557(Pt 2):635-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.062984. Epub 2004 Apr 2. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15064324 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological basis of acute inflammatory hyperaemia in the rat knee: roles of cyclo-oxygenase-1 and -2.J Physiol. 2002 Mar 1;539(Pt 2):579-87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013473. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11882689 Free PMC article.
-
Chemopreventive properties of a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in colon carcinogenesis, administered alone or in combination with celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):165-70. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782374
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced increase of prostaglandin E(2) is mediated by inducible nitric oxide synthase activation of the constitutive cyclooxygenase and induction of membrane-associated prostaglandin E synthase.J Immunol. 2001 Oct 1;167(7):3962-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.7.3962. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11564815
-
Dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: a reappraisal.Pharmacol Res. 2001 Dec;44(6):437-50. doi: 10.1006/phrs.2001.0872. Pharmacol Res. 2001. PMID: 11735348 Review.
Cited by
-
Can L(+)-lactate be used as a marker of experimentally induced inflammation in rats?Inflamm Res. 2010 Apr;59(4):315-21. doi: 10.1007/s00011-009-0107-6. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 19862479
-
Electroporation-enhanced transdermal diclofenac sodium delivery into the knee joint in a rat model of acute arthritis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Jun 27;12:1917-1930. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S161703. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29983546 Free PMC article.
-
Interdicting protease-activated receptor-2-driven inflammation with cell-penetrating pepducins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 17;108(20):8491-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017091108. Epub 2011 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21536878 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of synovial vascularity using contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography: correlation with histologic findings and mr imaging findings in arthritic rabbit knee model.Korean J Radiol. 2008 Jan-Feb;9(1):45-53. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.1.45. Korean J Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18253075 Free PMC article.
-
Oral phosphatidylcholine pretreatment alleviates the signs of experimental rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(2):R43. doi: 10.1186/ar2651. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19296835 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

