A synthetic A tail rescues yeast nuclear accumulation of a ribozyme-terminated transcript
- PMID: 15547135
- PMCID: PMC1370677
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7166704
A synthetic A tail rescues yeast nuclear accumulation of a ribozyme-terminated transcript
Abstract
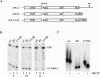
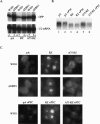
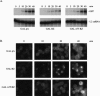
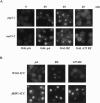
To investigate the role of 3' end formation in yeast mRNA export, we replaced the mRNA cleavage and polyadenylation signal with a self-cleaving hammerhead ribozyme element. The resulting RNA is unadenylated and accumulates near its site of synthesis. Nonetheless, a significant fraction of this RNA reaches the cytoplasm. Nuclear accumulation was relieved by insertion of a stretch of DNA-encoded adenosine residues immediately upstream of the ribozyme element (a synthetic A tail). This indicates that a 3' stretch of adenosines can promote export, independently of cleavage and polyadenylation. We further show that a synthetic A tail-containing RNA is unaffected in 3' end formation mutant strains, in which a normally cleaved and polyadenylated RNA accumulates within nuclei. Our results support a model in which a polyA tail contributes to efficient mRNA progression away from the gene, most likely through the action of the yeast polyA-tail binding protein Pab1p.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Uncoupling of mRNA 3' cleavage and polyadenylation by expression of a hammerhead ribozyme in yeast.J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27378-83. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7961648
-
Polyadenylation of rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 8;101(23):8581-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402888101. Epub 2004 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15173578 Free PMC article.
-
Polyadenylation of rRNA- and tRNA-based yeast transcripts cleaved by internal ribozyme activity.Curr Genet. 2003 Jul;43(4):255-62. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0401-8. Epub 2003 May 14. Curr Genet. 2003. PMID: 12748813
-
[Coordinated pathway of nuclear mRNA export reveled by the genetic analysis in yeast].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009 Dec;54(16 Suppl):2102-8. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009. PMID: 21089625 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
3'-end-forming signals of yeast mRNA.Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Dec;21(12):477-81. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(96)10057-8. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. PMID: 9009831 Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA quality control pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biosci. 2013 Sep;38(3):615-40. doi: 10.1007/s12038-013-9337-4. J Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23938393 Review.
-
Reporter mRNAs cleaved by Rnt1p are exported and degraded in the cytoplasm.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Nov;39(21):9357-67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr627. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21821655 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(A) RNA-binding proteins and polyadenosine RNA: new members and novel functions.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Sep-Oct;5(5):601-22. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1233. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24789627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense Transcription of Retrotransposons in Drosophila: An Origin of Endogenous Small Interfering RNA Precursors.Genetics. 2016 Jan;202(1):107-21. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.177196. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26534950 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(A) Polymerase and the Nuclear Poly(A) Binding Protein, PABPN1, Coordinate the Splicing and Degradation of a Subset of Human Pre-mRNAs.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jul;35(13):2218-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00123-15. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25896913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, N.P., Patel, S.S., Huang, L., Chalkley, R.J., Burlingame, A., Lutzmann, M., Hurt, E.C., and Rexach, M. 2002. Deciphering networks of protein interactions at the nuclear pore complex. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1: 930–946. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. (eds.). 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology, vol. 1. Wiley, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
