Transient overexpression of mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) is sufficient to stimulate mitochondrial DNA transcription, but not sufficient to increase mtDNA copy number in cultured cells
- PMID: 15547250
- PMCID: PMC534614
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh921
Transient overexpression of mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) is sufficient to stimulate mitochondrial DNA transcription, but not sufficient to increase mtDNA copy number in cultured cells
Abstract
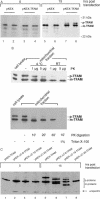
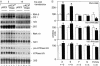
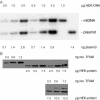
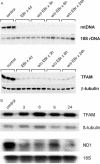
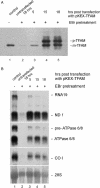
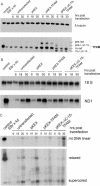
Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) stimulates transcription from mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) promoters in vitro and in organello. To investigate whether changes of TFAM levels also modulate transcription and replication in situ, the protein was transiently overexpressed in cultured cells. Mitochondrial mRNAs were significantly elevated at early time points, when no expansion of the TFAM pool was yet observed, but were decreased when TFAM levels had doubled, resemb-ling in vitro results. HEK cells contain about 35 molecules of TFAM per mtDNA. High levels of TFAM were not associated with increases of full-length mtDNA, but nucleic acid species sensitive to RNAse H increased. Stimulation of transcription was more evident when TFAM was transiently overexpressed in cells pre-treated with ethidium bromide (EBr) having lowered mtDNA, TFAM and mitochondrial transcript levels. EBr rapidly inhibited mtDNA transcription, while decay of mtDNA was delayed and preferentially slowly migrating, relaxed mtDNA species were depleted. In conclusion, we show that transcription of mtDNA is submaximal in cultured cells and that a subtle increase of TFAM within the matrix is sufficient to stimulate mitochondrial transcription. Thus, this protein meets all criteria for being a key factor regulating mitochondrial transcription in vivo, but other factors are necessary for increasing mtDNA copy number, at least in cultured cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Architectural role of mitochondrial transcription factor A in maintenance of human mitochondrial DNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):9823-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9823-9834.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15509786 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Tfam protects mitochondria against beta-amyloid-induced oxidative damage in SH-SY5Y cells.FEBS J. 2009 Jul;276(14):3800-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07094.x. Epub 2009 Jun 3. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19496804
-
Overexpression of mitochondrial transcription factor a ameliorates mitochondrial deficiencies and cardiac failure after myocardial infarction.Circulation. 2005 Aug 2;112(5):683-90. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.524835. Epub 2005 Jul 25. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 16043643
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A regulates mitochondrial transcription initiation, DNA packaging, and genome copy number.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep-Oct;1819(9-10):921-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22465614 Review.
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM): roles in maintenance of mtDNA and cellular functions.Mitochondrion. 2007 Feb-Apr;7(1-2):39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2006.11.017. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Mitochondrion. 2007. PMID: 17280879 Review.
Cited by
-
Core human mitochondrial transcription apparatus is a regulated two-component system in vitro.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 6;107(27):12133-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910581107. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20562347 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Control of Mitochondrial Function in the Vasculature.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Mar 4;7:28. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00028. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32195271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrially targeted ZFNs for selective degradation of pathogenic mitochondrial genomes bearing large-scale deletions or point mutations.EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Apr;6(4):458-66. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303672. Epub 2014 Feb 24. EMBO Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24567072 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Assessment of Mitochondrial DNA Maintenance by Depletion and Repopulation Using 2',3'-Dideoxycytidine in Cultured Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2615:229-240. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2922-2_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36807796
-
Mitochondrial retrograde signaling regulates neuronal function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 3;112(44):E6000-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505036112. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26489648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parisi M.A. and Clayton,D.A. (1991) Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science, 252, 965–969. - PubMed
-
- Falkenberg M., Gaspari,M., Rantanen,A., Trifunovic,A., Larsson,N.G. and Gustafsson,C.M. (2002) Mitochondrial transcription factors B1 and B2 activate transcription of human mtDNA. Nature Genet., 31, 289–294. - PubMed
-
- Dairaghi D.J., Shadel,G.S. and Clayton,D.A. (1995) Addition of a 29 residue carboxyl-terminal tail converts a simple HMG box-containing protein into a transcriptional activator. J. Mol. Biol., 249, 11–28. - PubMed
-
- Clayton D.A. (1982) Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell, 28, 693–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

