The chromosomally encoded cation diffusion facilitator proteins DmeF and FieF from Wautersia metallidurans CH34 are transporters of broad metal specificity
- PMID: 15547276
- PMCID: PMC529076
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.23.8036-8043.2004
The chromosomally encoded cation diffusion facilitator proteins DmeF and FieF from Wautersia metallidurans CH34 are transporters of broad metal specificity
Abstract
Genomic sequencing of the beta-proteobacterium Wautersia (previously Ralstonia) metallidurans CH34 revealed the presence of three genes encoding proteins of the cation diffusion facilitator (CDF) family. One, CzcD, was previously found to be part of the high-level metal resistance system Czc that mediates the efflux of Co(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) ions catalyzed by the CzcCBA cation-proton antiporter. The second CDF protein, FieF, is probably mainly a ferrous iron detoxifying protein but also mediated some resistance against other divalent metal cations such as Zn(II), Co(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) in W. metallidurans or Escherichia coli. The third CDF protein, DmeF, showed the same substrate spectrum as FieF, but with different preferences. DmeF plays the central role in cobalt homeostasis in W. metallidurans, and a disruption of dmeF rendered the high-level metal cation resistance systems Czc and Cnr ineffective against Co(II). This is evidence for the periplasmic detoxification of substrates by RND transporters of the heavy metal efflux family subgroup.
Figures
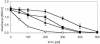
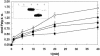
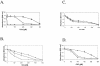


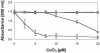
 ), AE128 dmeF::pLO2(pMOL30) (
), AE128 dmeF::pLO2(pMOL30) ( ), and AE128 dmeF::pLO2(pMOL30-14 ΔczcD) (○).
), and AE128 dmeF::pLO2(pMOL30-14 ΔczcD) (○).Similar articles
-
Characteristics of zinc transport by two bacterial cation diffusion facilitators from Ralstonia metallidurans CH34 and Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2004 Nov;186(22):7499-507. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.22.7499-7507.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15516561 Free PMC article.
-
CzcD is a heavy metal ion transporter involved in regulation of heavy metal resistance in Ralstonia sp. strain CH34.J Bacteriol. 1999 Nov;181(22):6876-81. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.22.6876-6881.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10559151 Free PMC article.
-
Cupriavidus metallidurans: evolution of a metal-resistant bacterium.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2009 Aug;96(2):115-39. doi: 10.1007/s10482-008-9284-5. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2009. PMID: 18830684 Review.
-
FieF (YiiP) from Escherichia coli mediates decreased cellular accumulation of iron and relieves iron stress.Arch Microbiol. 2005 Jan;183(1):9-18. doi: 10.1007/s00203-004-0739-4. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Arch Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15549269
-
Resistance to cadmium, cobalt, zinc, and nickel in microbes.Plasmid. 1992 Jan;27(1):17-28. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90003-s. Plasmid. 1992. PMID: 1741458 Review.
Cited by
-
High-level chromate resistance in Arthrobacter sp. strain FB24 requires previously uncharacterized accessory genes.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Sep 16;9:199. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-199. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19758450 Free PMC article.
-
Switch or funnel: how RND-type transport systems control periplasmic metal homeostasis.J Bacteriol. 2011 May;193(10):2381-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.01323-10. Epub 2011 Mar 11. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21398536 Free PMC article.
-
Cobalt Resistance via Detoxification and Mineralization in the Iron-Reducing Bacterium Geobacter sulfurreducens.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 26;11:600463. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.600463. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33324382 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the C-terminal domain of MamM, a magnetosome-associated protein from Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012 Aug 1;68(Pt 8):927-30. doi: 10.1107/S1744309112025638. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012. PMID: 22869124 Free PMC article.
-
Phenanthrene-Degrading and Nickel-Resistant Neorhizobium Strain Isolated from Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Rhizosphere of Medicago sativa L.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 4;12(8):1586. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081586. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloss, T., S. Clemens, and D. H. Nies. 2002. Characterization of the ZAT1p zinc transporter from Arabidopsis thaliana in microbial model organisms and reconstituted proteoliposomes. Planta 214:783-791. - PubMed
-
- Chao, Y., and D. Fu. 2004. Kinetic study of the antiport mechanism of an Escherichia coli zinc transporter, ZitB. J. Biol. Chem. 279:12043-12050. - PubMed
-
- Chao, Y., and D. Fu. 2004. Thermodynamic studies of the mechanism of metal binding to the Escherichia coli zinc transporter YiiP. J. Biol. Chem. 279:17173-17180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

