CP-31398, a putative p53-stabilizing molecule tested in mammalian cells and in yeast for its effects on p53 transcriptional activity
- PMID: 15548325
- PMCID: PMC534789
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5751-3-5
CP-31398, a putative p53-stabilizing molecule tested in mammalian cells and in yeast for its effects on p53 transcriptional activity
Abstract
Background: CP-31398 is a small molecule that has been reported to stabilize the DNA-binding core domain of the human tumor suppressor protein p53 in vitro. The compound was also reported to function as a potential anti-cancer drug by rescuing the DNA-binding activity and, consequently, the transcription activation function of mutant p53 protein in mammalian tissue culture cells and in mice.
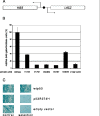
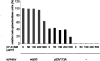
Results: We performed a series of gene expression experiments to test the activity of CP-31398 in yeast and in human cell cultures. With these cell-based assays, we were unable to detect any specific stimulation of mutant p53 activity by this compound. Concentrations of CP-31398 that were reported to be active in the published work were highly toxic to the human H1299 lung carcinoma and Saos-2 cell lines in our experiments.
Conclusion: In our experiments, the small molecule CP-31398 was unable to reactivate mutant p53 protein. The results of our in vivo experiments are in agreement with the recently published biochemical analysis of CP-31398 showing that this molecule does not bind p53 as previously claimed, but intercalates into DNA.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

