The novel highly lipophilic topoisomerase I inhibitor DB67 is effective in the treatment of liver metastases of murine CT-26 colon carcinoma
- PMID: 15548354
- PMCID: PMC1531650
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04139
The novel highly lipophilic topoisomerase I inhibitor DB67 is effective in the treatment of liver metastases of murine CT-26 colon carcinoma
Abstract
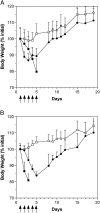
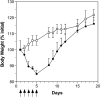
Colorectal carcinoma occurs in 1 of 20 individuals in most developed countries. The relapse after resection with metastatic liver disease is a major cause of death. 7-t-Butyldimethylsilyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (DB67) has been incorporated into liposomes allowing for intravenous (i.v.) administration. A preclinical efficacy study of liposomal DB67 was performed using the colon carcinoma CT-26 cell line. The therapeutic dose for DB67 and liposomal DB67 was found to be 7 mg/kg per day using the qdx5/1 schedule. The results are compared with those obtained with irinotecan. The treatment with liposomal DB67 administered intravenously was more effective in reducing the weight and volume of primary spleen tumors and the weight and extent of liver metastases than free DB67 or liposomal DB67 administered intraperitoneally, but less effective than irinotecan. When the primary tumor was resected, treatment with liposomal DB67 administered intravenously was more effective in reducing the weight and extent of liver metastases than DB67 or liposomal DB67 administered intraperitoneally, and irinotecan. DB67 showed a higher accumulation in spleen and liver after its i.v. administration in liposomal form compared with its free or liposomal form administered intraperitoneally. DB67 and liposomal DB67 are more effective than irinotecan in the treatment of liver metastases after resection of the primary tumor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of intestinal toxic effects and intensification of irinotecan's therapeutic efficacy against murine colon cancer liver metastases by oral administration of the lipopeptide JBT 3002.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Sep;4(9):2053-63. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9748119
-
Protracted dosing of the lipophilic camptothecin analogue AR-67 in non-small cell lung cancer xenografts and humans.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;74(1):45-54. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2472-2. Epub 2014 May 8. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24807458
-
Liposomal irinotecan: formulation development and therapeutic assessment in murine xenograft models of colorectal cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 1;10(19):6638-49. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0221. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15475454
-
Detailed distribution of NK012, an SN-38-incorporating micelle, in the liver and its potent antitumor effects in mice bearing liver metastases.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 1;16(19):4822-31. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1467. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20807756
-
Encapsulation of the topoisomerase I inhibitor GL147211C in pegylated (STEALTH) liposomes: pharmacokinetics and antitumor activity in HT29 colon tumor xenografts.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Dec;4(12):3077-82. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9865923
Cited by
-
Camptothecin (CPT) and its derivatives are known to target topoisomerase I (Top1) as their mechanism of action: did we miss something in CPT analogue molecular targets for treating human disease such as cancer?Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 1;7(12):2350-2394. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29312794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug development in advanced colorectal cancer: challenges and opportunities.Curr Oncol Rep. 2009 May;11(3):175-85. doi: 10.1007/s11912-009-0026-2. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19336009 Review.
-
A review of the past, present, and future directions of neoplasia.Neoplasia. 2005 Dec;7(12):1039-46. doi: 10.1593/neo.05793. Neoplasia. 2005. PMID: 16354585 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Antitumor and antimetastatic effects of licochalcone A in mouse models.J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 Aug;88(8):829-38. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0625-2. Epub 2010 Apr 11. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20383690
-
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of AR-67, a lactone stable camptothecin analogue, in cancer patients with solid tumors.Invest New Drugs. 2019 Dec;37(6):1218-1230. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00744-0. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Invest New Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30820810 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cunningham D, Findlay M. The chemotherapy of colon cancer can no longer be ignored. Eur J Cancer. 1996;29A:2077–2079. - PubMed
-
- Rougier P, Paillot B, LaPlanche A, Morvan F, Seitz JF, Rekacewicz C, Laplaige P, Jacob J, Grandjowan S, Tigaud JM, Fabri MC, Luboinski M, Ducreux M. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) continuous intravenous infusion compared with bolus administration. Final results of a randomised trial in metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1997;33:1789–1793. - PubMed
-
- Pitot HC, Wender DB, O'Connel MJ, Schroeder G, Goldberg RM, Rubin J, Mailliard JA, Knost JA, Kirschling RJ, Lewitt R, Windschitl HE. Phase II trial of irinotecan in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2910–2919. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson P, Carmichael J, Alakl M, Gruia G, Awad L, Rougier P. Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;25:1041–1047. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Pyrhonen S, James RD, Punt CJ, Hickish TF, Heikkila R, Johannesen TB, Strarkhammar H, Topham CA, Awad L, Jacques C, Herait P. Randomised trial of irinotecan plus supportive care versus supportive care alone after fluorouracil failure for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1998;352:1413–1418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
