Lonidamine causes inhibition of angiogenesis-related endothelial cell functions
- PMID: 15548359
- PMCID: PMC1531654
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04133
Lonidamine causes inhibition of angiogenesis-related endothelial cell functions
Abstract
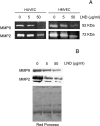
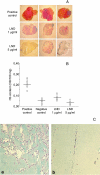
The aim of this study was to assess whether lonidamine (LND) interferes with some steps in angiogenesis progression. We report here, for the first time, that LND inhibited angiogenic-related endothelial cell functions in a dose-dependent manner (1-50 microg/ml). In particular, LND decreased proliferation, migration, invasion, and morphogenesis on matrigel of different endothelial cell lines. Zymographic and Western blot analysis assays showed that LND treatment produced a reduction in the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 by endothelial cells. Vessel formation in a matrigel plug was also reduced by LND. The viability, migration, invasion, and matrix metalloproteinase production of different tumor cell lines were not affected by low doses of LND (1-10 microg/ml), whereas 50 microg/ml LND, which corresponds to the dose used in clinical management of tumors, triggered apoptosis both in endothelial and tumor cells. Together, these data demonstrate that LND is a compound that interferes with endothelial cell functions, both at low and high doses. Thus, the effect of LND on endothelial cell functions, previously undescribed, may be a significant contributor to the antitumor effect of LND observed for clinical management of solid tumors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The transforming growth factor-beta family members bone morphogenetic protein-2 and macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 as mediators of the antiangiogenic activity of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 15;11(12):4610-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2210. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15958647
-
Pseudolarix acid B inhibits angiogenesis by antagonizing the vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated anti-apoptotic effect.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 24;499(3):219-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.063. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15381043
-
Nicotine induces cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in association with tumor-associated invasion and angiogenesis in gastric cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2005 Nov;3(11):607-15. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0106. Mol Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16317086
-
Gabexate mesilate inhibits colon cancer growth, invasion, and metastasis by reducing matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jul 1;10(13):4517-26. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0084. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15240544
-
The Potential of Lonidamine in Combination with Chemotherapy and Physical Therapy in Cancer Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 11;12(11):3332. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113332. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33187214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of EGFR-targeted polymer blend nanocarriers for combination paclitaxel/lonidamine delivery to treat multi-drug resistance in human breast and ovarian tumor cells.Mol Pharm. 2011 Feb 7;8(1):185-203. doi: 10.1021/mp1002653. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Mol Pharm. 2011. PMID: 20942457 Free PMC article.
-
The lonidamine derivative H2-gamendazole reduces cyst formation in polycystic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):F492-F506. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00095.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35979967 Free PMC article.
-
ROS homeostasis and metabolism: a critical liaison for cancer therapy.Exp Mol Med. 2016 Nov 4;48(11):e269. doi: 10.1038/emm.2016.119. Exp Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27811934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of metabolic cancer therapy on tumor microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 13;12:1046630. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1046630. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36582801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the past, present, and future directions of neoplasia.Neoplasia. 2005 Dec;7(12):1039-46. doi: 10.1593/neo.05793. Neoplasia. 2005. PMID: 16354585 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ianniello GP, De Cataldis G, Comella P, Scarpati MD, Maiorino A, Brancaccio L, Cioffi R, Lombardi A, Carnicelli P, Tinessa V. Cisplatin, epirubicin, and vindesine with or without lonidamine in the treatment of inoperable nonsmall lung carcinoma: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Cancer. 1996;78:63–69. - PubMed
-
- De Lena M, Lorusso V, Bottalico C, Brandi M, De Mitrio A, Catino A, Guida M, Latorre A, Leone B, Vallejo C, Gargano G. Revertant and potentiating activity of lonidamine in patients with ovarian cancer previously treated with platinum. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:3208–3213. - PubMed
-
- Nisticò C, Garufi C, Milella M, D'Ottavio AM, Vaccaio A, Fabi A, Terzoli E. Weekly epirubicin plus lonidamine in advanced breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1999;56:233–237. - PubMed
-
- De Lena M, Lo Russo V, Latorre A, Canizza G, Gargano G, Caporosso L, Guida M, Catino A, Crucitta E, Sambiasi D, Mazzei A. Paclitaxel, cisplatin and lonidamine in advanced ovarian cancer. A phase II study. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:364–368. - PubMed
-
- Di Cosimo S, Ferretti G, Papaldo P, Carlini P, Fabi A, Cognetti F. Lonidamine efficacy and safety in clinical trials for the treatment of solid tumors. Drugs Today. 2003;39:157–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
