Fractionation of the epithelial apical junctional complex: reassessment of protein distributions in different substructures
- PMID: 15548593
- PMCID: PMC545905
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0827
Fractionation of the epithelial apical junctional complex: reassessment of protein distributions in different substructures
Abstract
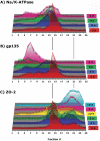
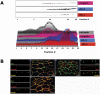
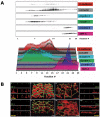
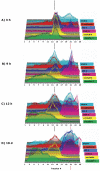
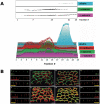
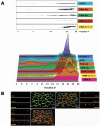
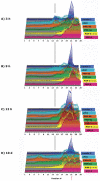
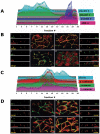
The epithelial apical junctional complex (AJC) is an important regulator of cell structure and function. The AJC is compartmentalized into substructures comprising the tight and adherens junctions, and other membrane complexes containing the membrane proteins nectin, junctional adhesion molecule, and crumbs. In addition, many peripheral membrane proteins localize to the AJC. Studies of isolated proteins indicate a complex map of potential binding partners in which there is extensive overlap in the interactions between proteins in different AJC substructures. As an alternative to a direct search for specific protein-protein interactions, we sought to separate membrane substructures of the AJC in iodixanol density gradients and define their protein constituents. Results show that the AJC can be fractured into membrane substructures that contain specific membrane and peripheral membrane proteins. The composition of each substructure reveals a more limited overlap in common proteins than predicted from the inventory of potential interactions; some of the overlapping proteins may be involved in stepwise recruitment and assembly of AJC substructures.
Figures




References
-
- Aberle, H., Butz, S., Stappert, J., Weissig, H., Kemler, R., and Hoschuetzky, H. (1994). Assembly of the cadherin-catenin complex in vitro with recombinant proteins. J. Cell Sci. 107, 3655-3663. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, J. M., Van Itallie, C. M., and Fanning, A. S. (2004). Setting up a barrier at the apical junction complex. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16, 140-145. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni, G., Martinez-Estrada, O. M., Orsenigo, F., Cordenonsi, M., Citi, S., and Dejana, E. (2000). Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 20520-20526. - PubMed
-
- Brajenovic, M., Joberty, G., Kuster, B., Bouwmeester, T., and Drewes, G. (2004). Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human Par protein complexes reveals an interconnected protein network. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 12804-12811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

