Analysis of mutant phenotypes and splicing defects demonstrates functional collaboration between the large and small subunits of the essential splicing factor U2AF in vivo
- PMID: 15548596
- PMCID: PMC545896
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0768
Analysis of mutant phenotypes and splicing defects demonstrates functional collaboration between the large and small subunits of the essential splicing factor U2AF in vivo
Abstract
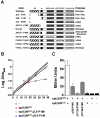
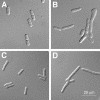
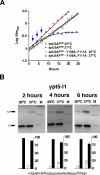
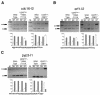
The heterodimeric splicing factor U2AF plays an important role in 3' splice site selection, but the division of labor between the two subunits in vivo remains unclear. In vitro assays led to the proposal that the human large subunit recognizes 3' splice sites with extensive polypyrimidine tracts independently of the small subunit. We report in vivo analysis demonstrating that all five domains of spU2AFLG are essential for viability; a partial deletion of the linker region, which forms the small subunit interface, produces a severe growth defect and an aberrant morphology. A small subunit zinc-binding domain mutant confers a similar phenotype, suggesting that the heterodimer functions as a unit during splicing in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. As this is not predicted by the model for metazoan 3' splice site recognition, we sought introns for which the spU2AFLG and spU2AFSM make distinct contributions by analyzing diverse splicing events in strains harboring mutations in each partner. Requirements for the two subunits are generally parallel and, moreover, do not correlate with the length or strength of the 3' pyrimidine tract. These and other studies performed in fission yeast support a model for 3' splice site recognition in which the two subunits of U2AF functionally collaborate in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo requirement of the small subunit of U2AF for recognition of a weak 3' splice site.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(21):8183-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00350-06. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16940179 Free PMC article.
-
The splicing factor U2AF small subunit is functionally conserved between fission yeast and humans.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 May;24(10):4229-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4229-4240.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15121844 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic mRNA profiling reveals compensatory mechanisms for the requirement of the essential splicing factor U2AF.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Feb;31(4):652-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01000-10. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21149581 Free PMC article.
-
The evolutionary conservation of the splicing apparatus between fission yeast and man.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995;(33):226-8. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995. PMID: 8643378 Review.
-
U2AF homology motifs: protein recognition in the RRM world.Genes Dev. 2004 Jul 1;18(13):1513-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.1206204. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15231733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo requirement of the small subunit of U2AF for recognition of a weak 3' splice site.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(21):8183-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00350-06. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16940179 Free PMC article.
-
A BBP-Mud2p heterodimer mediates branchpoint recognition and influences splicing substrate abundance in budding yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 May;36(8):2787-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn144. Epub 2008 Mar 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18375978 Free PMC article.
-
Sde2 is an intron-specific pre-mRNA splicing regulator activated by ubiquitin-like processing.EMBO J. 2018 Jan 4;37(1):89-101. doi: 10.15252/embj.201796751. Epub 2017 Sep 25. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 28947618 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific recognition of the 3' splice site of INS intron 1.Hum Genet. 2010 Oct;128(4):383-400. doi: 10.1007/s00439-010-0860-1. Epub 2010 Jul 14. Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20628762 Free PMC article.
-
RRM domain of Arabidopsis splicing factor SF1 is important for pre-mRNA splicing of a specific set of genes.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Jul;36(7):1083-1095. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2140-1. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28401337
References
-
- Abovich, N., Liao, X., and Rosbash, M. (1994). The yeast MUD2 protein: an interaction with PRP11 defines a bridge between commitment complex and U2 snRNP addition. Genes Dev. 8, 843-854. - PubMed
-
- Beales, M., Flay, N., McKinney, R., Habara, Y., Ohshima, Y., Tani, T., and Potashkin, J. (2000). Mutations in the large subunit of U2AF disrupt pre-mRNA splicing, cell cycle progression and nuclear structure. Yeast 16, 1001-1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

